CNN Architectures¶
1 AlexNet¶
- \(227\times 227\) inputs, RGB
- 5 Convolutional layers
- Max Pooling
- 3 fully-connected layers
- ReLU nonlinearities
Use Local response normalization
- 大部分的内存占用和浮点运算发生在早期的卷积层中
- 几乎所有的参数都出现在全连接层中
2 ZF Net¶
larger version of AlexNet
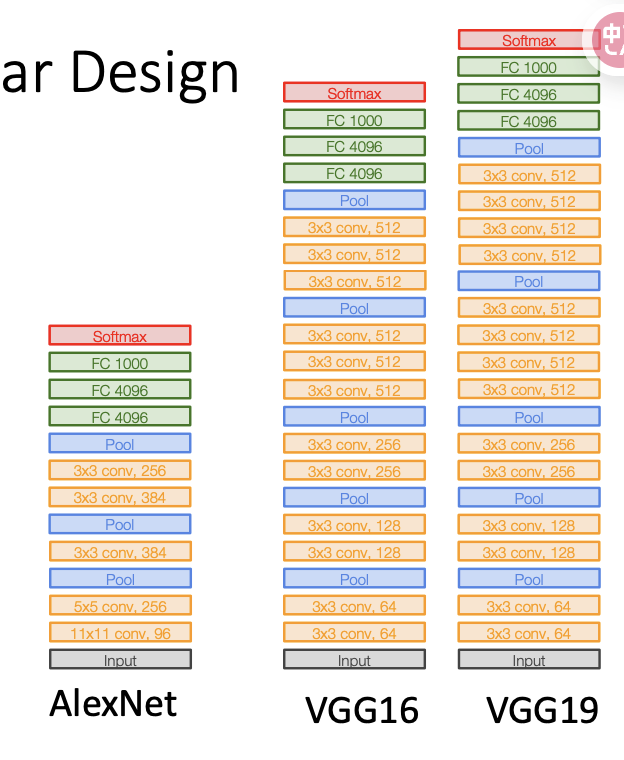
3 VGG: Deeper Networks, Regular Design¶
VGG Design rules: - 所有卷积层 3 3,步长1,pad 1 - 所有池化层,2 2, 步长2 - 池化之后,通道数量增加一倍
\(Conv(5\times5)\)和两层\(Conv(3\times 3)\)有相同大小的感受野,但是两层3* 3的卷积对应的参数量和浮点运算数量更少
可以在两层之间插入非线性层
Much Bigger network!!!
4 Google Net¶
4.1 Stem Network¶
at the start,积极地对图像进行下采样
4.2 Inception module¶
Local unit with parallel branches
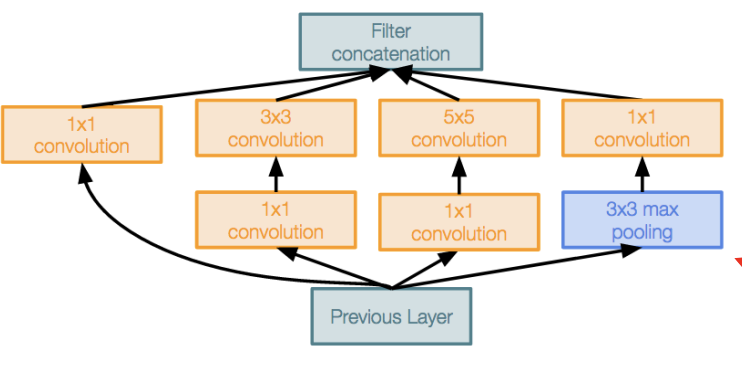
四条分支使用不同大小的卷积核和池化层进行计算
使用一个\(1\times 1\)的卷积核
4.3 Global Average Pooling¶
最后不展开张量来破坏空间信息,而是使用平均池化的方式
No large FC layers at the end! Instead uses global average pooling to collapse spatial dimensions, and one linear layer to produce class scores

4.4 Auxiliary Classifiers¶
神经网络太深导致使用最后输出的loss无法很好地运行
在中间某几层添加辅助分类器,用于在这时候对图像进行分类并得到loss
5 ResNet¶
更深的神经网络往往更难进行优化,不容易模拟更浅的神经网络
解决方案:Change the network so learning identity functions with extra layers is easy!
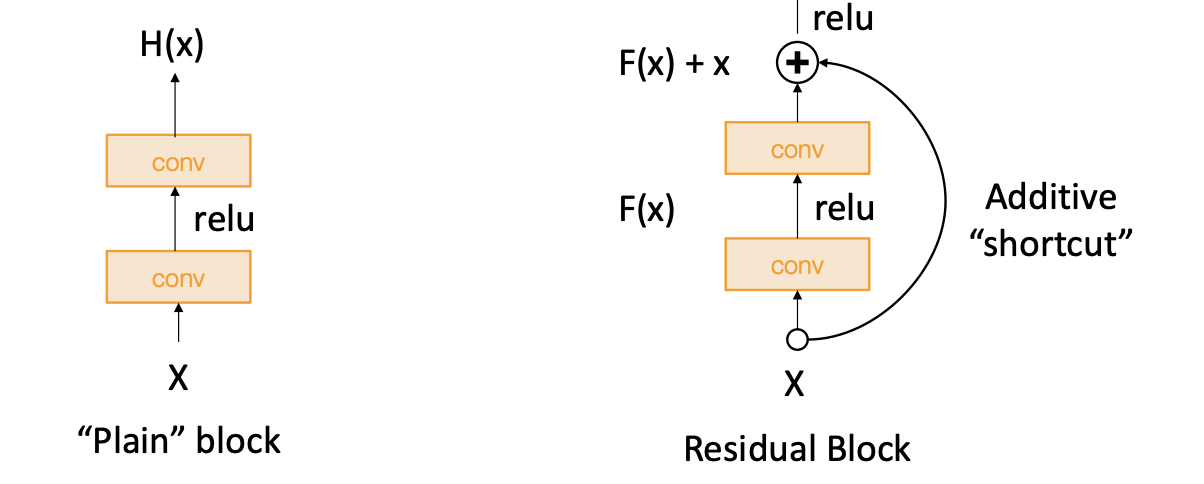
将输入添加到第二个卷积层的输出中,使其更容易模拟恒等函数
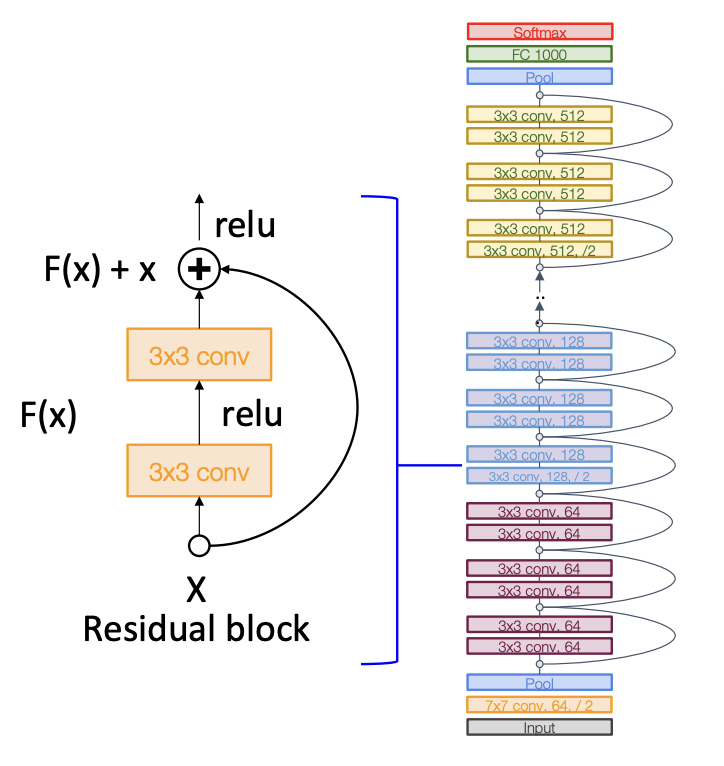
5.1 Bottleneck Block¶

More layers, less computational cost, 更强的非线性
- 能够训练非常深的网络
- 深度的网络比浅的网络的表现更好

6 Improving ResNets: ResNeXt¶
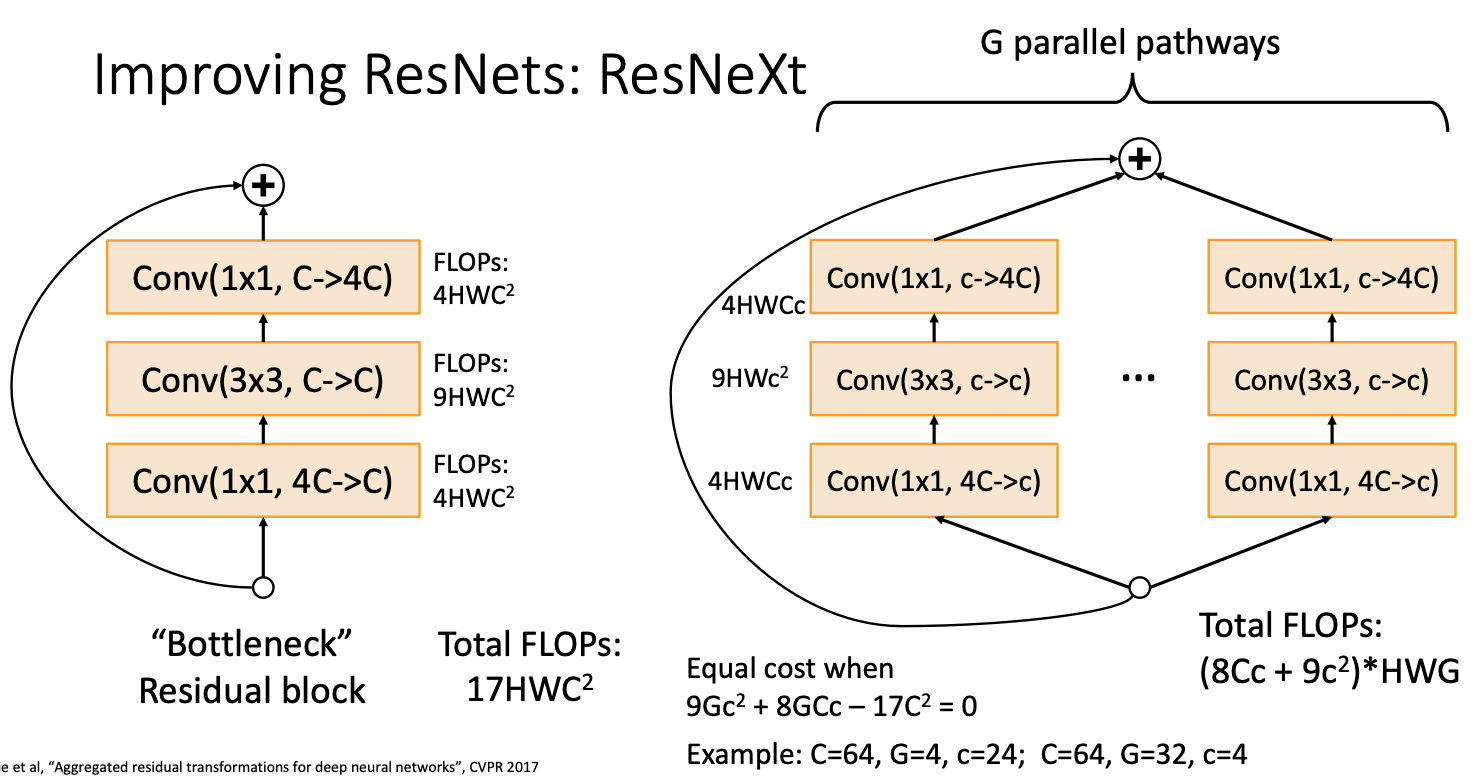
每一组有自己的卷积核,在保证计算效率的同时,减少计算量和参数量