Advanced SQL¶
1 Accessing SQL from a Programming Language¶
- 不是所有的 查询都能够用SQL语言表达
- Non-declarative actions: 例如打印报告,与用户交互,发送查询结果至图形用户界面等不能再SQL中完成
从高级语言访问数据库,主要是以下两种方式:
- API(Application Program Interface) -- A general-purpose program can connect to and communicate with a database server using a collection of functions.
函数库
- Embedded SQL -- provides a means by which a program can interact with a database server.
把 SQL 语句嵌入到语言内
- The SQL statements are translated at compile time into function calls.
- At runtime, these function calls connect to the database using an API that provides dynamic SQL facilities
1.1 JDBC and ODBC¶
API 使程序能够与数据库服务器沟通
应用程序调用: - 和数据库服务器建立连接 - 将SQL命令发送到服务器 - 一个一个取回结果元组至程序变量中
SQL 与 C 语言存在鸿沟(如 select 得到的是集合,但是 C 语言没有这种类型)会返回指针/迭代器
- ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) works with C, C++, C#
- JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) works with Java
通过类定义,将数据库操作封装到 Java 内 - Embedded SQL in C
- SQLJ - embedded SQL in Java
- JPA(Java Persistence API) - OR mapping of Java
1.1.1 JDBC¶
JDBC is a Java API for communicating with database systems supporting SQL.
public static void JDBCexample(String dbid, String userid, String passwd)
{
try {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@db.yale.edu:2000:univdb", userid, passwd);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
… Do Actual Work ….
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
catch (SQLException sqle) {
System.out.println("SQLException : " + sqle);
}
}
- Open a connection
- Create a “statement” object
- Execute queries using the Statement object to send queries and fetch results
- Exception mechanism to handle errors
Example
- Update to database
- Execute query and fetch and print results
- Getting result fields:
- Dealing with Null values
Prepared Statement
Prepared Statement
PreparedStatement pStmt = conn.prepareStatement(
"insert into instructor values(?,?,?,?)");
pStmt.setString(1, "88877");
pStmt.setString(2, "Perry");
pStmt.setString(3, "Finance");
pStmt.setInt(4, 125000);
pStmt.executeUpdate();
pStmt.setString(1, "88878");
pStmt.executeUpdate();
setString, setInt 就是把第几个占位符设置为参数,并 executeUpdate 进行插入。
SQL Injection
Always use prepared statements when taking an input from the user and adding it to a query. NEVER create a query by concatenating strings which you get as inputs. 当从用户处获取输入并将其添加到查询中时,始终使用prepared statement。永远不要通过connnectioin作为输入的字符串来创建查询。
SQL 注入攻击。
Suppose query is constructed using select * from instructor where name = ’" + name + “ ’
Suppose the user, instead of entering a name, enters: X’ or ’Y’ = ’Y
then the resulting string of the statement becomes: select * from instructor where name = ’" + "X’ or ’Y’ = ’Y" + “’
which is: select * from instructor where name = ’X’ or ’Y’ = ’Y’
User could have even used
X’; update instructor set salary = salary + 10000;
then select * from instructor where name = ’X’; update instructor set salary = salary + 10000;
总是使用prepared statements,用户输入作为参数
Metadata Features
-
ResultSet metadata
-
Database metadata
Example
DatabaseMetaData dbmd = conn.getMetaData(); ResultSet rs = dbmd.getColumns(null, "univdb", "department", "%"); // Arguments to getColumns: Catalog, Schema-pattern, Table-pattern, // and Column-Pattern // Returns: One row for each column; row has a number of attributes // such as COLUMN_NAME, TYPE_NAME while( rs.next()) { System.out.println(rs.getString("COLUMN_NAME"), rs.getString("TYPE_NAME");
Transaction Control in JDBC
- Can turn off automatic commit on a connection
conn.setAutoCommit(false); - Transactions must then be committed or rolled back explicitly
conn.commit();orconn.rollback(); conn.setAutoCommit(true)turns on automatic commit.
所有的数据库功能都是通过 Java 封装好的类来实现的。
other JDBC features
- 调用函数和procedure
- 处理large的数据类型
- getBlob() and getClob() that are similar to the getString() method, but return objects of type Blob and Clob, respectively
- get data from these objects by getBytes()
- associate an open stream with Java Blob or Clob object to update large objects。将开放流与Java Blob或Clob对象关联以更新大型对象
1.1.2 SQLJ¶
JDBC is overly dynamic, errors cannot be caught by compiler
SQLJ: embedded SQL in Java
#sql iterator deptInfoIter ( String dept name, int avgSal);
deptInfoIter iter = null;
#sql iter = { select dept_name, avg(salary) as avgSal from instructor
group by dept name };
while (iter.next()) {
String deptName = iter.dept_name();
int avgSal = iter.avgSal();
System.out.println(deptName + " " + avgSal);
}
iter.close();
#sql 标识,最后会被编译器转化为 Java 的类。
1.1.3 ODBC¶
Open database conectivity - standard for application program to communicate with a database server. - application program interface (API) to - open a connection with a database, - send queries and updates, - get back results.
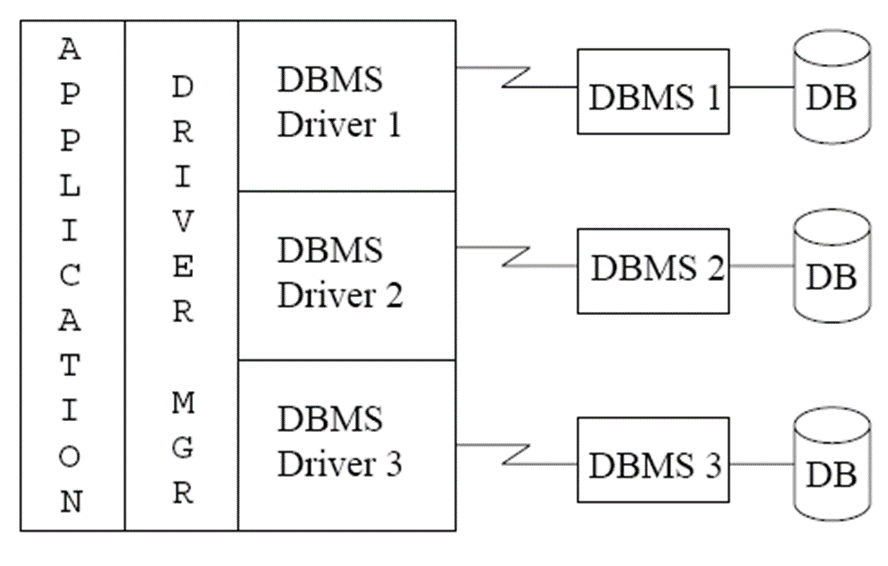
Each database system supporting ODBC provides a "driver" library that must be linked with the client program.
当client program 发起一个ODBC API 调用,库中的代码与数据库建立联系并执行操作获得结果
Opens database connection using SQLConnect(). Parameters for SQLConnect: - connection handle, - the server to which to connect - the user identifier, - password
SQL_NTS denotes previous argument is a null-terminated string.
用于指示某个参数是一个以空字符(\0)结尾的字符串(即 C 语言中的 null-terminated string)
Example
int ODBCexample()
{
RETCODE error;
HENV env; /* environment */
HDBC conn; /* database connection */
SQLAllocEnv(&env);
SQLAllocConnect(env, &conn);
SQLConnect(conn, “db.yale.edu", SQL_NTS, "avi", SQL_NTS, "avipasswd", SQL_NTS);
{ ... Do actual work ... }
SQLDisconnect(conn);
SQLFreeConnect(conn);
SQLFreeEnv(env);
}
同一个数据库可能服务于多个用户,而且使用的编程语言可能不同,如字符串的结束标志可能也不同,因此需要用 SQL_NTS 标识。
- Program sends SQL commands to database by using
SQLExecDirect - Result tuples are fetched using
SQLFetch() SQLBindCol()binds C language variables to attributes of the query result- When a tuple is fetched, its attribute values are automatically stored in corresponding C variables.
- Arguments to SQLBindCol()
- ODBC stmt variable, attribute position in query result
- The type conversion from SQL to C.
- The address of the variable.
- For variable-length types like character arrays,
- The maximum length of the variable
- Location to store actual length when a tuple is fetched.
- Note: A negative value returned for the length field indicates null value
Example
Main body of program
char deptname[80];
float salary;
int lenOut1, lenOut2;
HSTMT stmt;
char * sqlquery = "select dept_name, sum (salary) from instructor group by dept_name";
SQLAllocStmt(conn, &stmt);
error = SQLExecDirect(stmt, sqlquery, SQL_NTS);
if (error == SQL SUCCESS) {
SQLBindCol(stmt, 1, SQL_C_CHAR, deptname , 80, &lenOut1);
SQLBindCol(stmt, 2, SQL_C_FLOAT, &salary, 0 , &lenOut2);
while (SQLFetch(stmt) == SQL_SUCCESS) {
printf (" %s %g\n", deptname, salary);
}
}
SQLFreeStmt(stmt, SQL_DROP);
char deptname[11]; 才能定义十个元组。如果结果为空,则
lenOut 为 -1.
ODBC Prepared Statements
- SQL statement prepared: compiled at the database
- To prepare a statement
SQLPrepare(stmt, <SQL String>); - To bind parameters
SQLBindParameter(stmt, <parameter#>, ... type information and value omitted for simplicity..) - To execute the statement
retcode = SQLExecute(stmt);
- To prepare a statement
- Can have placeholders: e.g.
insert into account values(?,?,?) - Repeatedly executed with actual values for the placeholders
SQL injection

More ODBC Features
- Metadata features
- finding all the relations in the database and
- finding the names and types of columns of a query result or a relation in the database.
- By default, each SQL statement is treated as a separate transaction that is committed automatically.
- Can turn off automatic commit on a connection
SQLSetConnectOption(conn, SQL_AUTOCOMMIT, 0)} - Transactions must then be committed or rolled back explicitly by
SQLTransact(conn, SQL_COMMIT)orSQLTransact(conn, SQL_ROLLBACK)
- Can turn off automatic commit on a connection
ODBC Conformance Levels
Conformance levels specify subsets of the functionality defined by the standard. - Core - Level 1 requires support for metadata querying - Level 2 requires ability to send and retrieve arrays of parameter values and more detailed catalog information.
SQL Call Level Interface (CLI) standard similar to ODBC interface, but with some minor differences.
1.1.4 Embedded SQL¶
A language to which SQL queries are embedded is referred to as a host language, and the SQL structures permitted in the host language comprise embedded SQL.
如把 SQL 嵌入到 C 语言,那么 C 语言是 host.
在编译前,有一个预编译器,将 SQL 语句翻译。
EXEC SQL statement is used in the host language to identify embedded SQL request to the preprocessor (in Java, # SQL { ... };)
在执行SQL statement之前,程序必须首先连接到数据库
EXEC-SQL connect to server user user-name using password;
```
Variables of the host language can be used within embedded SQL statements.They are preceded by a colon (:) to distinguish from SQL variables (e.g., :credit_amount )
Host Variables used as above must be declared within DECLARE section, as illustrated below. The syntax for declaring the variables, however, follows the usual host language syntax.
```c
EXEC-SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION
int credit-amount ;
EXEC-SQL END DECLARE SECTION;
To write an embedded SQL query, we use the
declare c cursor for <SQL query>
statement. The variable c is used to identify the query
Example
From within a host language, find the ID and name of students who have completed more than the number of credits stored in variable credit_amount in the host langue
The open statement for our example is as follows:
该语句使数据库系统执行查询并将结果保存在一个临时关系中。查询在执行open语句时使用host language 变量 credit-amount的值。The fetch statement causes the values of one tuple in the query result to be placed on host language variables.
A variable called SQLSTATE in the SQL communication area (SQLCA) gets set to '02000' to indicate no more data is available
The close statement causes the database system to delete the temporary relation that holds the result of the query
updates through embedded SQL Embedded SQL expressions for database modification (update, insert, and delete)
Can update tuples fetched by cursor by declaring that the cursor is for update
然后通过在游标上执行取操作来遍历元组,取完每个元组后执行以下代码
Issues with Embedded SQL
- Mark the start point and end point of Embedded SQL
EXEC SQL <statement>; //C - Communication between database and programming language e.g. SQLCA、SQLDA
- Address the mismatching issue between SQL and host lanugage.
Handle result (set) with cursor Mapping of basic data types e.g. SQL: Date \(\rightarrow\) C: char(12)
Example
insert、delete、update、select(single record)
main( )
{ EXEC SQL INCLUDE SQLCA; //声明段开始
EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION;
char account_no [11]; //host variables(宿主变量)声明
char branch_name [16];
int balance;
EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION;//声明段结束
EXEC SQL CONNECT TO bank_db USER Adam Using Eve;
scanf (“%s %s %d”, account_no, branch_name, balance);
EXEC SQL insert into account
values (:account_no, :branch_name, :balance);
If (SQLCA.sqlcode ! = 0) printf ( “Error!\n”);
else printf (“Success!\n”);
}
两点不平衡:没有集合;没有 NULL;没有日期类型
可以在编译时进行类型检查,但 ODBC 只有在运行时才有。
- Static: Embedded SQL statements( include relation names and attribute names) are hard coded in program.
- Dynamic:Embedded SQL statements are built at run time
2 Procedural Constructs in SQL¶
SQL provides a module language
Permits definition of procedures in SQL, with if-then-else statements, for and while loops, etc.
Stored Procedures
- Can store procedures in the database
- then execute them using the call statement
- permit external applications to operate on the database without knowing about internal
2.1 Procedures and Functions¶
函数和存储过程允许将 “业务逻辑” 存储在数据库中,并通过 SQL 语句执行。 这些可以通过 SQL 的过程组件或外部编程语言(如 Java、C 或 C++)来定义。这里介绍的语法是由 SQL 标准定义的,大多数数据库实现的是该语法的非标准版本。
2.2 SQL Functions¶
Example

SQL 函数的返回值可以是一个 table.
Example

2.3 SQL Procedures¶
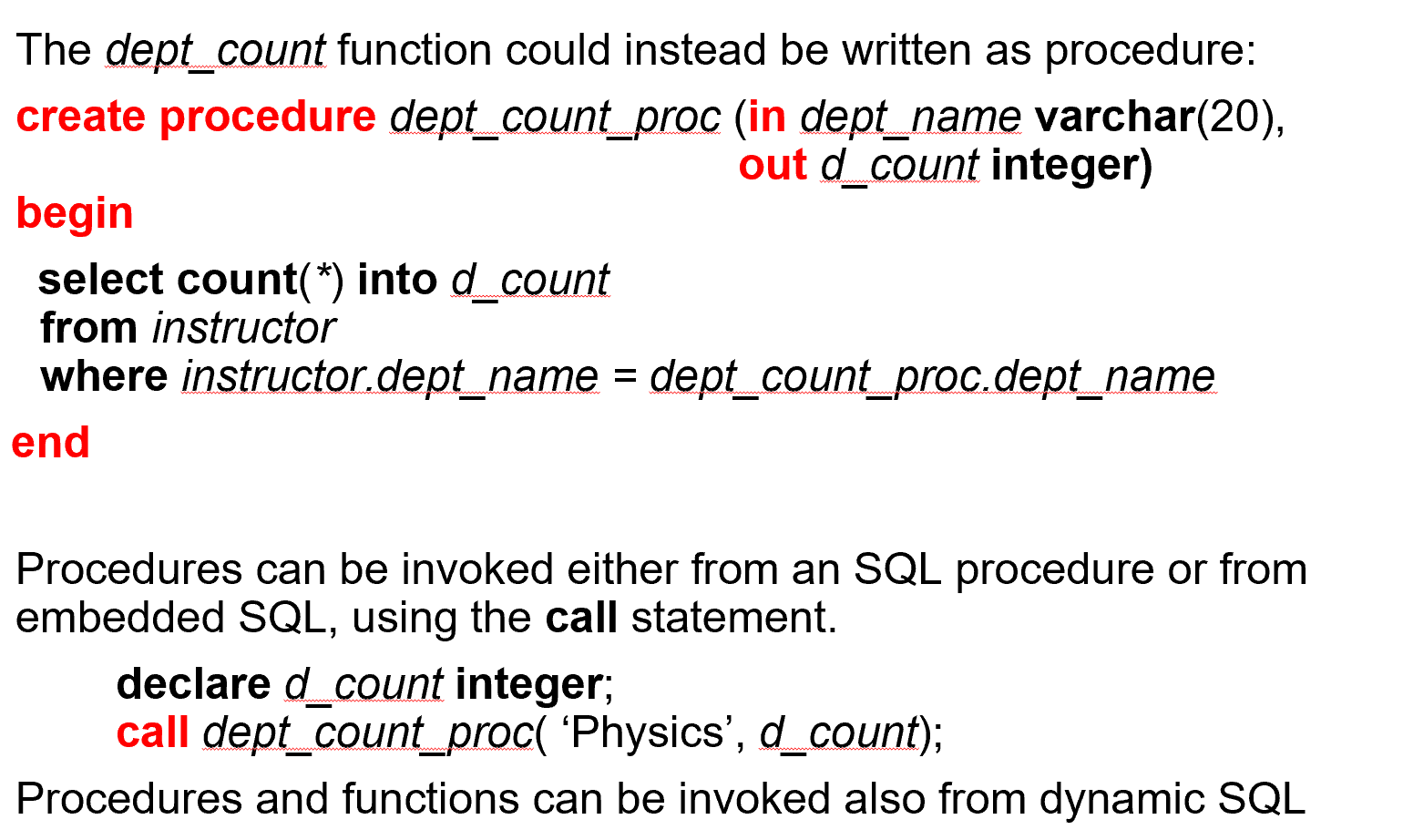
dept_count 函数也可以写成存储过程的形式:
有输入参数(in)和输出参数(out)
Example
2.4 Procedural Constructs¶
Compound statement: begin ... end,
- May contain multiple SQL statements between
beginandend. -
Local variables can be declared within a compound statements
-
Whileandrepeatstatements
e.g. -
r 表示返回的每一行Forloop Permits iteration over all results of a query e.g.
-
Conditional statements
Example procedure

2.5 External Language Functions/Procedures¶
SQL 可以访问由 C 语言定义的函数(过程)
Example
可能比较危险,放在虚拟机(Java)或者独立的线程
2.5.1 External language Routines¶
外部语言函数 / 过程的优点:
在许多操作中更高效,且具有更强的表达能力。
缺点:
实现函数的代码可能需要加载到数据库系统中,并在数据库系统的地址空间中执行。
存在意外损坏数据库结构的风险以及安全风险,可能会让用户访问到未经授权的数据。
也有一些替代方案,它们能提供良好的安全性,但可能会导致性能稍差。
当效率比安全性更重要时,会在数据库系统的空间中直接执行。
2.5.2 Security with External¶
- To deal with security problems¶
使用沙盒技术即使用像 Java 这样的安全语言,它无法用于访问或破坏数据库代码的其他部分。或者,在单独的进程中运行外部语言函数 / 过程,且无法访问数据库进程的内存。通过进程间通信来传递参数和结果。这两种方法都会产生性能开销。许多数据库系统支持上述两种方法,以及在数据库系统地址空间中直接执行。
3 Triggers¶
A trigger is a statement that is executed automatically by the system as a side effect of a modification to the database.
Trigger - ECA rule
* E: Event ( insert, delete ,update)
* C: Condition
A*: Action
To design a trigger mechanism, we must:
- Specify the conditions under which the trigger is to be executed.
- Specify the actions to be taken when the trigger executes.
Example
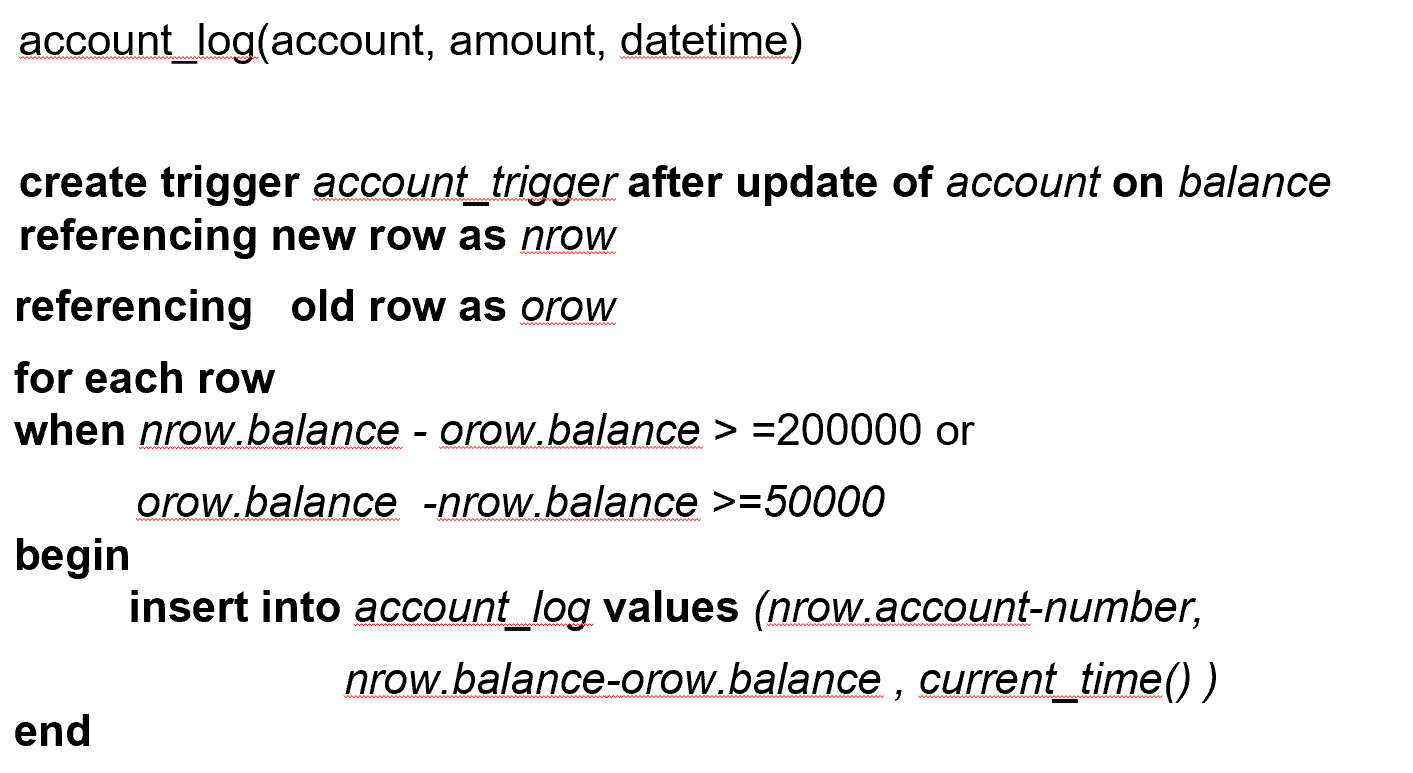
time_slot_id Example


这里 time_slot_id 不是主键,因此删除不会引起其他影响。但我们可以设计一个触发器,用来检查当前课程的 time_slot_id 是否在表内。
第二个触发器表示,time_slot_id 已经被删完了,但依然有课程在引用,就要 rollback.
- Triggering event can be insert, delete or update
- Triggers on update can be restricted to specific attributes
e.g. after(before) update of takes on grade - Values of attributes before and after an update can be referenced
- referencing old row as: for deletes and updates
- referencing new row as: for inserts and updates
Trigger to Maintain credits_earned value

如果本来挂科,或者没有成绩,更新后不再挂科而且有成绩,就把学分加上去。
要慎用触发器,用在刀刃上,可能会引发连锁反应。
Instead of executing a separate action for each affected row, a single action can be executed for all rows affected by a transaction
- Use
for each statementinstead offor each row - Use
referencing old tableorreferencing new tableto refer to temporary tables (called transition tables) containing the affected rows - Can be more efficient when dealing with SQL statements that update a large number of rows
Example
