Relational Modeling¶
Basic Structure: Formally, given sets \(D_1,D_2,\cdots,D_n\) a relation r is a subset of \(D_1\times D_2\times \cdots \times D_n\). Thus a relation is a set of n-tuple \((a_1,a_2,…,a_n)\) where each \(a_i∈D_i\).
\(A_1,A_2,…,A_n\) are attributes. \(R=(A_1,A_2,…,A_n)\) is a relation schema(有序的).
e.g. instructor = (ID, name, dept_name, salary).
A relation instance 关系实例 r defined over schema R is denoted by \(r(R)\).
因为关系是一个集合,所以关系都是无序的
Attributes
- The set of allowed values for each attribute is called the domain of the attribute 值域
- Attribute values are (normally) required to be atomic (原子的); that is, indivisible
- the special value null is a member of every domain 空值是任意一个值域的元素
- 空值会导致许多操作的定义的complications
1 Database Schema¶
- Database schema -- is the logical structure of the database.
- Database instance -- is a snapshot of the data in the database at a given instant in time.
2 Keys¶
- \(K \nsubseteq R\)
- K is a superkey (超键) of R if values for K are sufficient to identify (唯一确定) a unique tuple of each possible relation r(R)
e.g. {ID} or{ID,name}
- Superkey K is a candidate key (候选键) if K is minimal.
即 K 中没有冗余属性
- primary key 是从candidaate key 中挑选出来的一个。不能为空,不能重复
- Foreign key (外键) Relation r1 may include among its attributes the primary key of another relation r2. This attribute is called a foreign key from r1, referencing r2.
类似于指针,外键限制就是关系 r1 引用的主键必须在关系 r2 中出现。
- Referential integrity (参照完整性)
类似于外键限制,但不局限于主键。
Example
 - course 指课程信息,无论是否开课,都会有其定义。
- section 表示教学班,真正开课时就有相应的实例。(类比于高铁的列车号,和每天对应的班次)
- teachers 具体教哪个教学班的老师
- takes 表示学生注册课程
- time_slot 表示一门课的具体上课时间段,如数据库在周一 3, 4, 5 节; 周一 7, 8 节。
- 上图中红线表示引用完整性的约束;黑线表示外键约束。
- course 指课程信息,无论是否开课,都会有其定义。
- section 表示教学班,真正开课时就有相应的实例。(类比于高铁的列车号,和每天对应的班次)
- teachers 具体教哪个教学班的老师
- takes 表示学生注册课程
- time_slot 表示一门课的具体上课时间段,如数据库在周一 3, 4, 5 节; 周一 7, 8 节。
- 上图中红线表示引用完整性的约束;黑线表示外键约束。
3 Relational Query Language¶
"Pure" Langueges 三者等价 - Relational algebra 关系代数 - Tuple relational calculus 元组关系演算 - Domain relational calculus 域关系演算
3.1 Relational Algebra¶
6 basic operators: - select: \(\sigma\) 横向选择 - project: \(\Pi\) 纵向选择 - union: ∪ 集合并 - set difference: − 集合差 - Cartesian product(笛卡尔积): × - rename:\(\rho\)
3.1.1 Select¶
Example
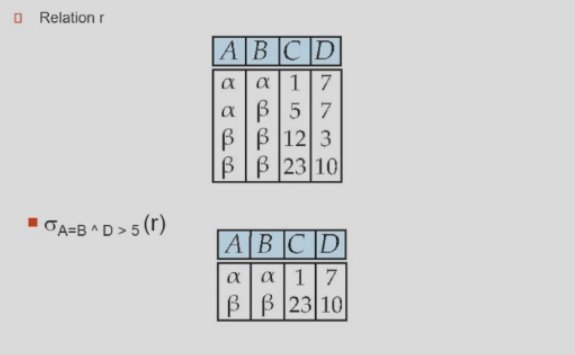
对关系进行操作,结果仍然是个关系
\(\sigma_p(r)= {t|t\in r ~and ~ p(t)}\),where \(p\) is called selection predict
从严格的元组的角度来讲,需要进行去重操作
3.1.2 Project¶
The project operation is a unary operation that returns its argument relation, with certain attributes left out.
\(\Pi_{A_1,A_2,…,A_k}(r)\) where \(A_i\) are attribute names and r is a relation name.
The result is defined as the relation of k columns obtained by erasing the columns that are not listed. 会对结果进行去重。
Example
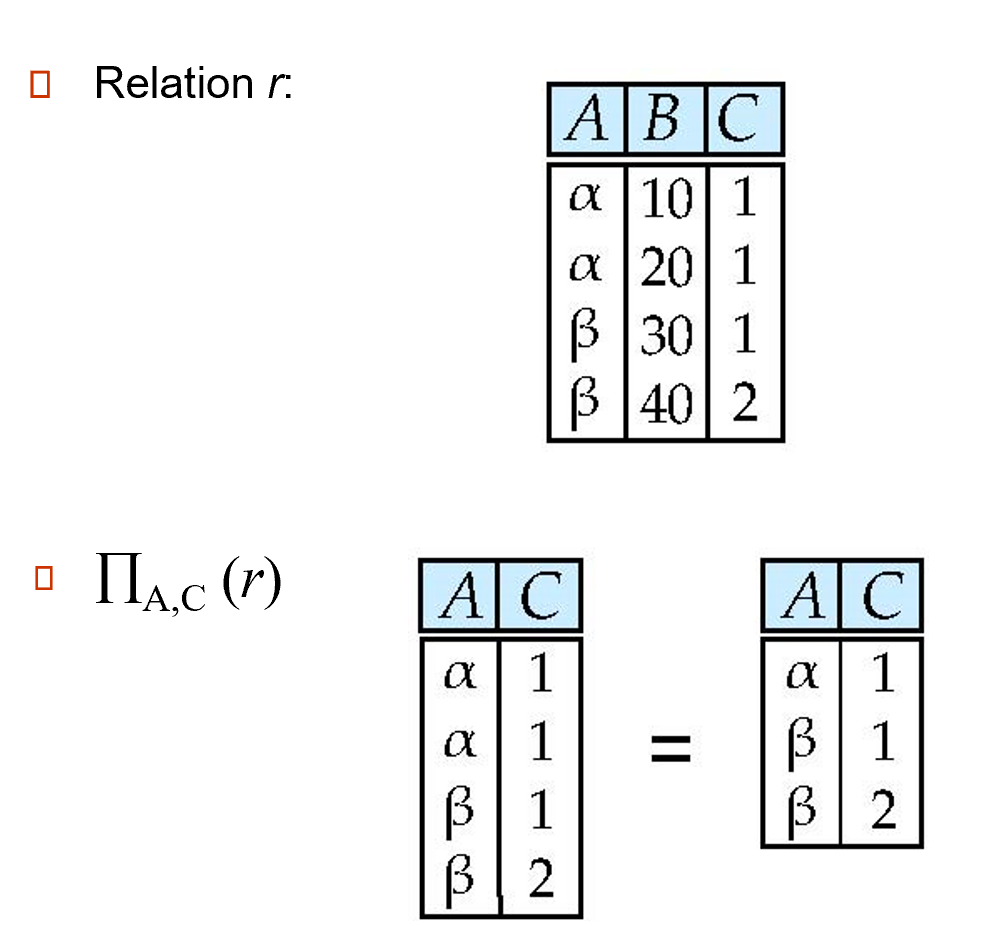
3.1.3 Union¶
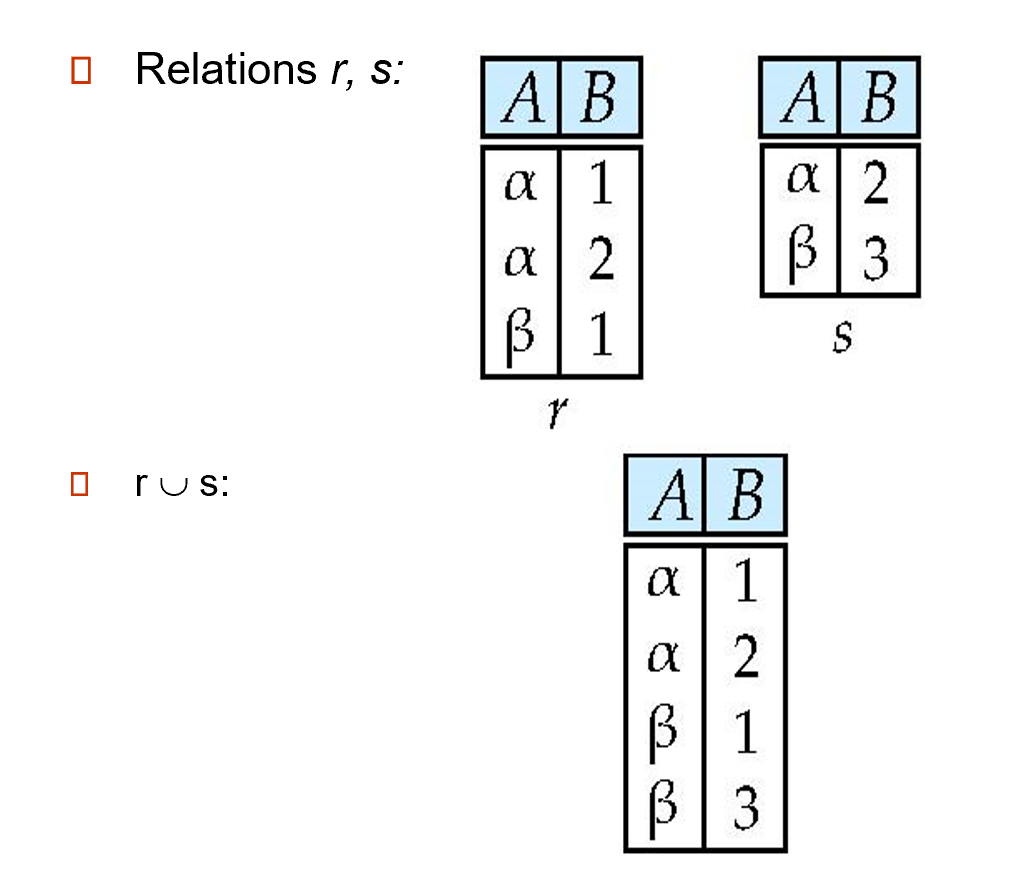
The union operation allows us to combine two relations.
\(r\cup s = \{t| t\in r \ or \ t\in s\}\)
- \(r\) and \(s\) must have the same arity (元数) (same number f attributes)
- The attribute domains must be compatible
当属性有关联类型时,对于每个输入 \(i\), 两个输入关系的第 \(i\) 个属性的类型必须相同。
Projection Example
3.1.4 Set Difference¶
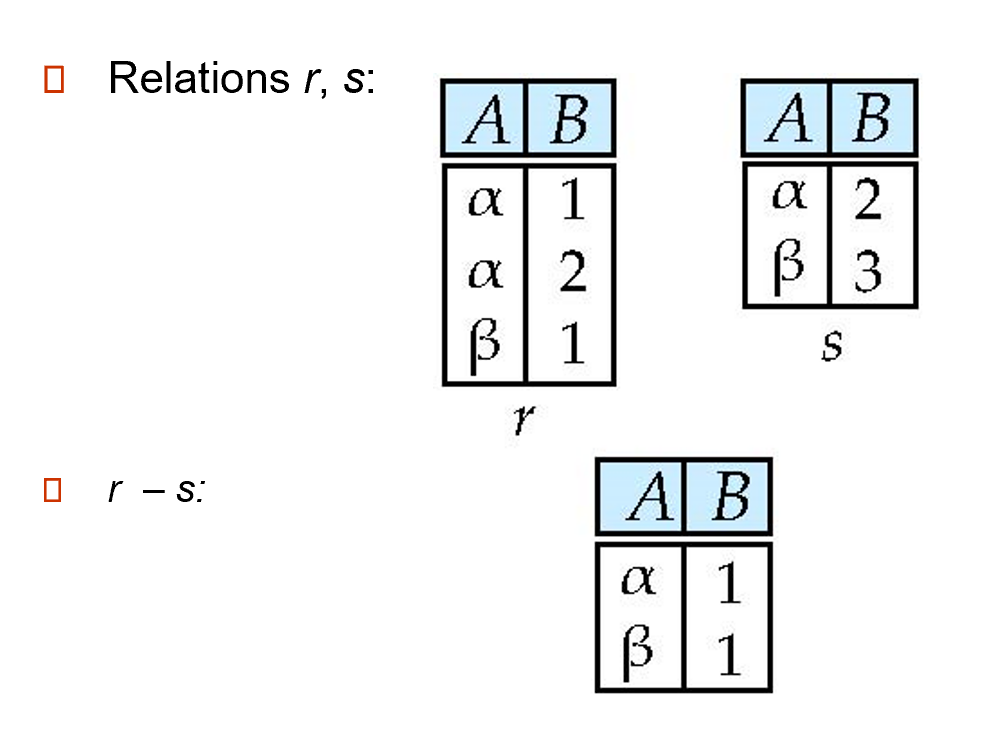
The set-difference operation allows us to find tuples that are in one relation but are not in another.
\(r-s=\{t|t\in r\ and\ t\notin s\}\)
Set differences must be taken between compatible relations.
Projection Example
3.1.5 Cartesian-Product¶
The Cartesian-product operation (denoted by \(\times\)) allows us to combine information from any two relations.
\(r\times s =\{t\ q|t\in r\ and\ q\in s\}\)
Projection Example

3.1.6 Rename=n¶
Allows us to refer to a relation by more than one name.
\(\rho_X(E)\)
Composition of Operations 1
Find the names of all instructors in the Physics department, along with the course_id of all courses they have taught.

这两条语句含义一样,但第二条我们先进行了一次 select, 条目少了更高效。
Composition of Operations 2
Find the largest salary in the university.
- find instructor salaries that are less than some other instructor salary (i.e. not maximum)
using a copy of instructor under a new name \(d\).
\(\prod_{instructor.salary}(\sigma_{instructor.salary<d.salary}(instructor \times \rho_d(instructor)))\) - find the largest salary
\(\prod_{instructor}-\prod_{instructor.salary}(\sigma_{instructor.salary}<d.salary(instructor\times \rho_d(instructor)))\)
我们第一步将两个关系拼起来之后,找出不是最大工资的(找出所有前一个工资小于后一个工资的),最后用全集减掉即可。
不是所有的查询都可以用关系代数表达式表达出来的
!!! note Formal Definition
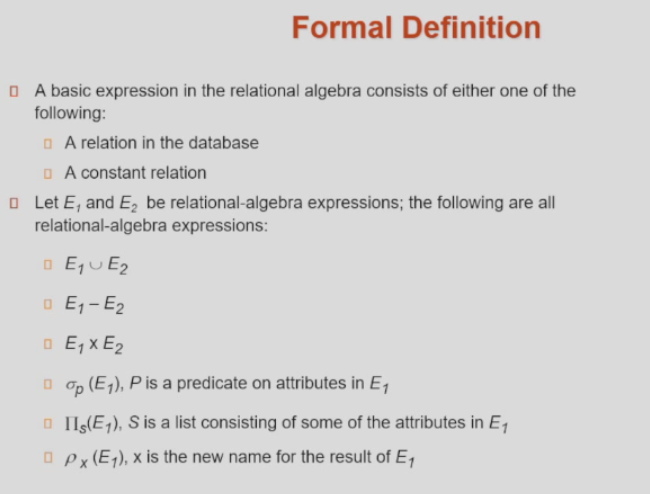
3.2 Additional Operations¶
- Set intersection: \(r \cap s\)
- Natural join: \(r\bowtie s\)
- Assignment: \(\leftarrow\)
- Outer join : \(r \rtimes s\), \(r \ltimes s\), \(r\)⟗\(s\)
- Division Operator: \(r \div s\)
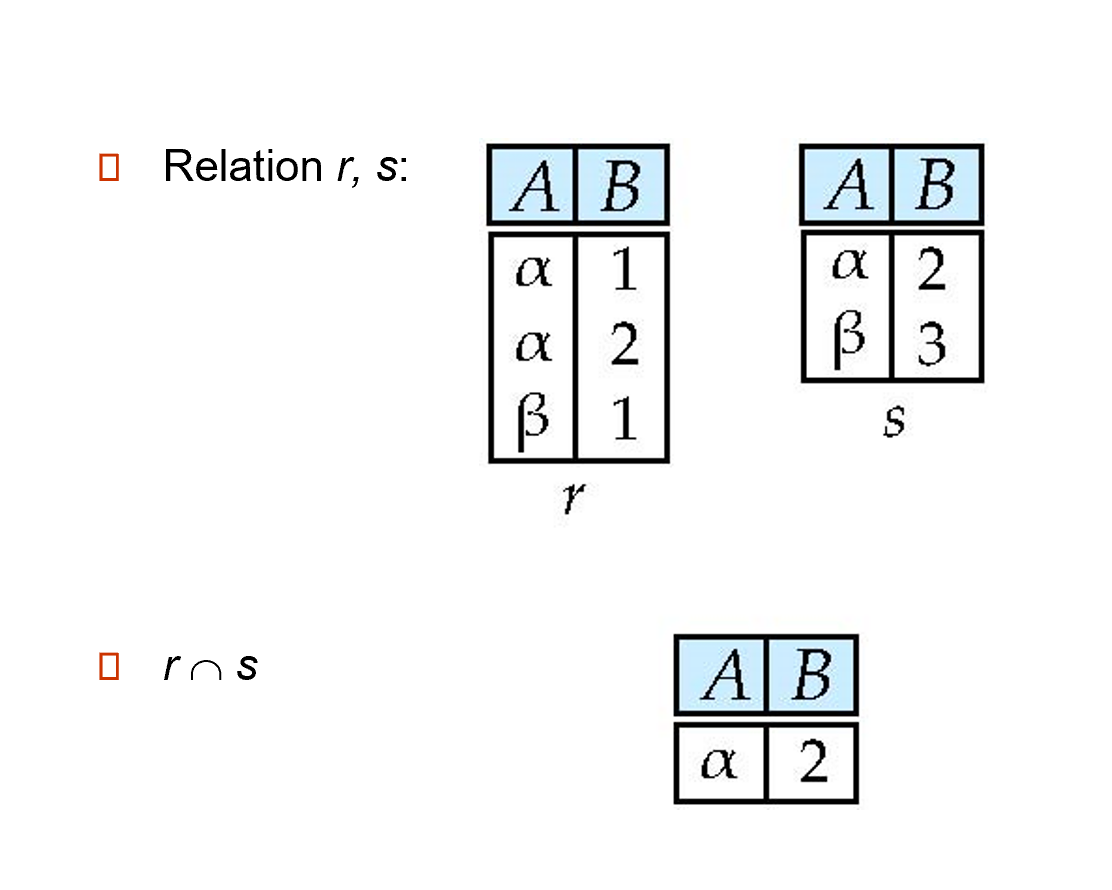
3.2.1 Set-Intersection¶
The set-intersection operation allows us to find tuples that are in both the input relations.
\(r\cap s=\{t| t\in r\ and\ t\in s\}\)
- \(r, s\) have the same arity
- attributes of \(r\) and s are compatible
Set-Intersection Operation Example
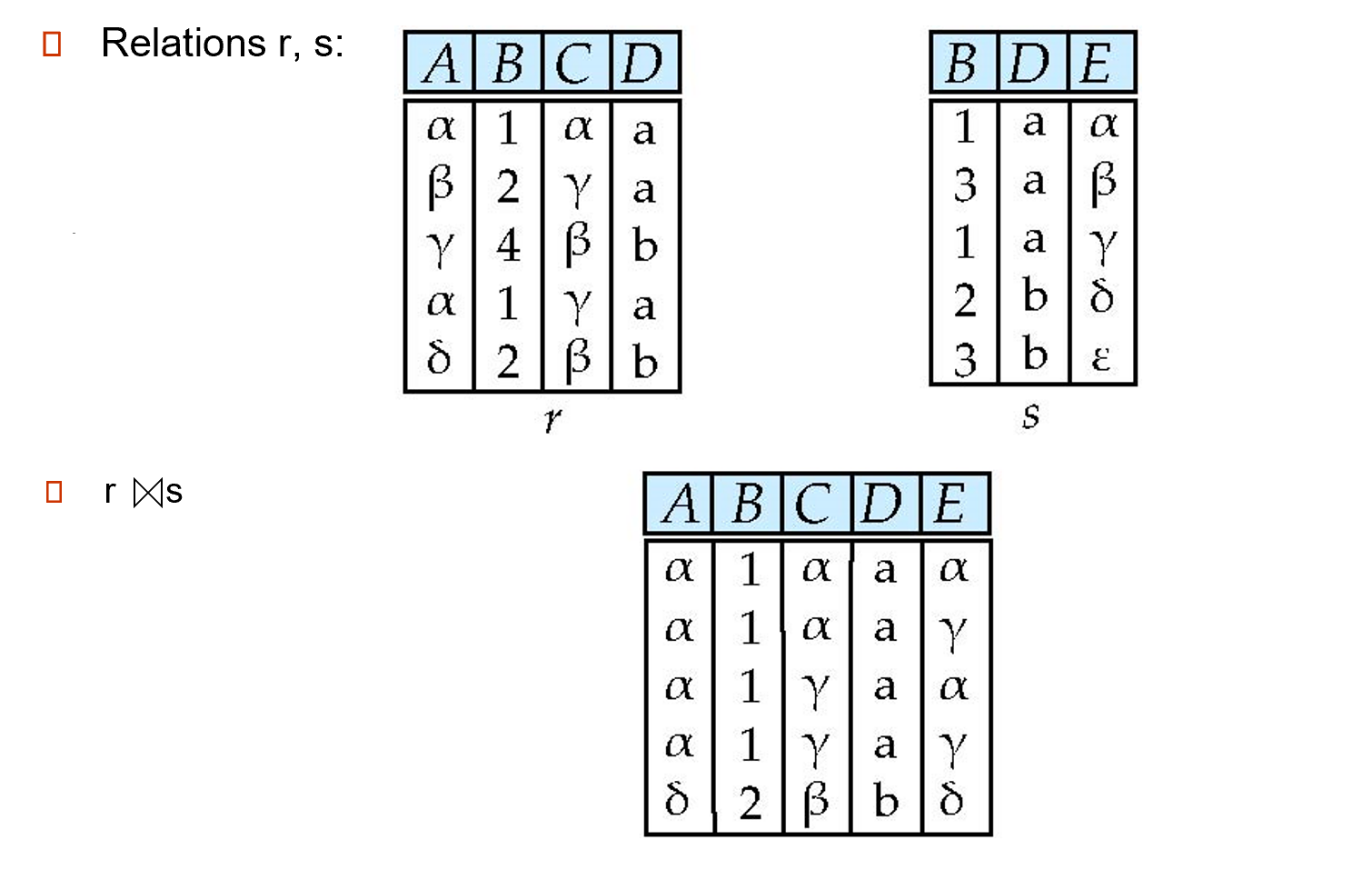
3.2.2 Natural-Join Operation¶
Let r and s be relations on schemas R and S respectively. Then, \(r\bowtie s\) is a relation on schema \(R \cup S\) obtained as follows:
- Consider each pair of tuples \(t_r\) from \(r\) and \(t_s\) from \(s\).
- If \(t_r\) and \(t_s\) have the same value on each of the attributes in \(R \cap S\), add a tuple $t $ to the result, where
- \(t\) has the same value as \(t_r\) on \(r\)
- \(t\) has the same value as \(t_s\) on \(s\)
即共同属性要有相同的值,才能在笛卡尔积后的结果中保留。
对乘法的扩展,相当于先 \(\times\) 再 select, 最后 project.
Natural join is associatve 组合,commutative交换
Natural Join Example
- Theta Join
\(r\bowtie_\theta s=\sigma_\theta (r\times s)\)
条件连接
3.2.3 Outer Join¶
Computes the join and then adds tuples form one relation that does not match tuples in the other relation to the result of the join.
Uses null values:
- null signifies that the value is unknown or does not exist
- All comparisons involving null are (roughly speaking) false by definition
Outer join can be expressed using basic operations.
- \(r\rtimes s=(r\bowtie s)\cup (r-\cap_R(r\bowtie s)\times \{null,\ldots,null\})\)
- \(r\ltimes s=(r\bowtie s)\cup \{null,\ldots,null\}\times (s-\cap_R(r\bowtie s))\)
- \(r\)⟗\(s\) \(=(r\bowtie s)\cup (r-\cap_R(r\bowtie s))\times \{(null, \ldots)\}\cup\{(null,\ldots,null)\}\times (s-\cap_s(r\bowtie s))\)
Outer Join Example


3.2.4 Assignment Operation¶
The assignment operation(\(\leftarrow\)),提供了一个表达复杂查询的方式
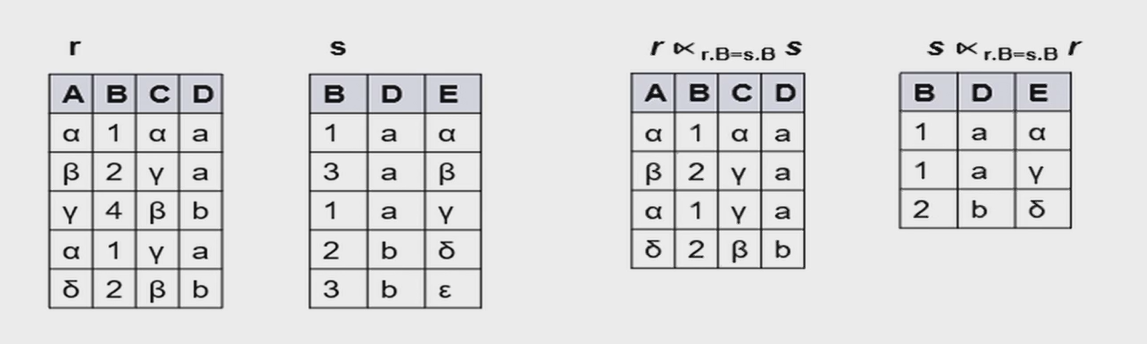
3.2.5 Semijoin 半连接¶
\(r\ltimes_\theta s\) 保留 \(r\) 中能与 \(s\) 相连的元组。相当于对\(r\)进行筛选
Semijoin Example
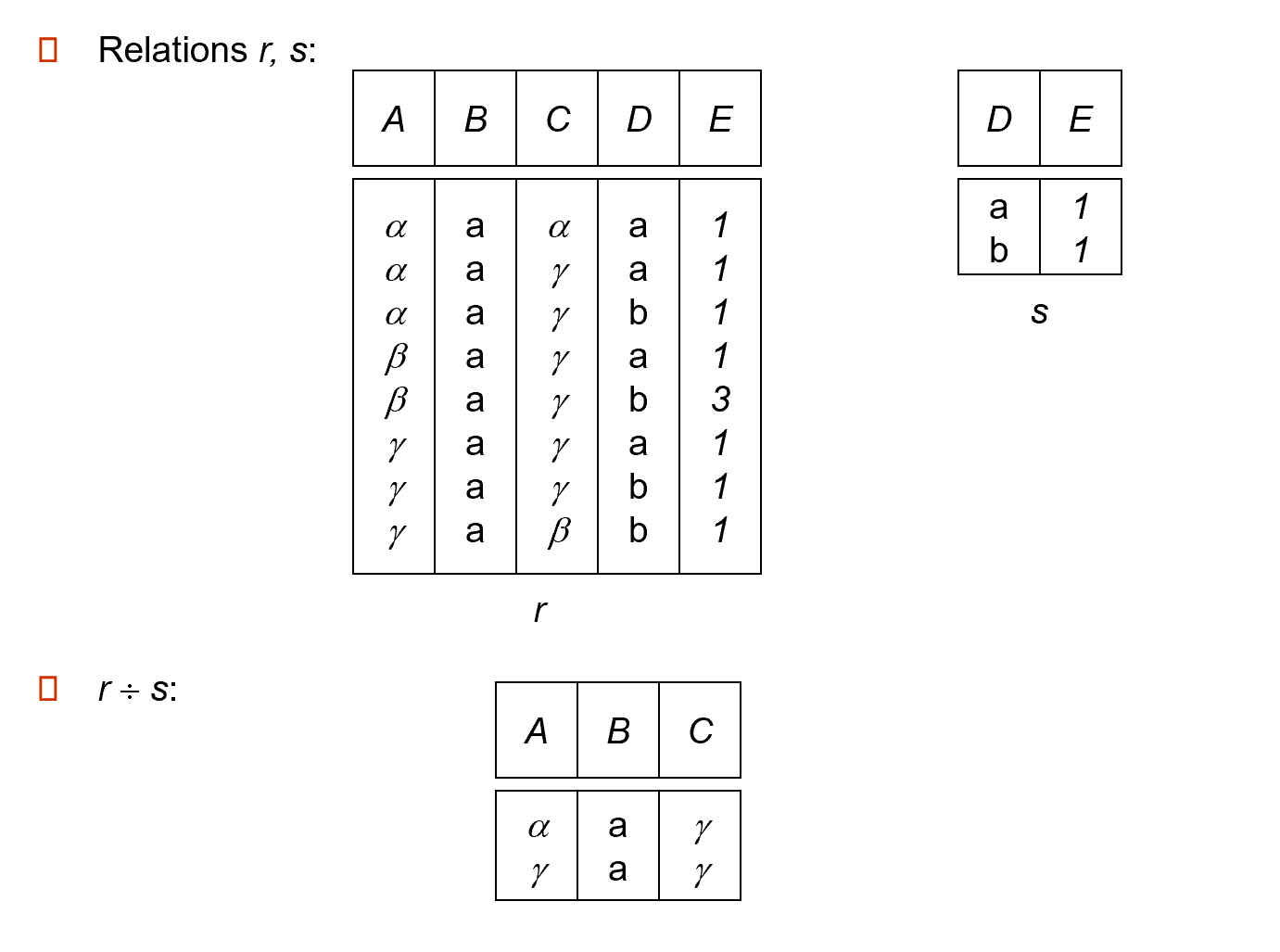
3.2.6 Division¶
Given relations \(r(R)\) and \(s(S)\), such that \(S \subset R\), \(r\div s\) is the largest relation \(t(R-S)\) such that \(t\times s \subsetneqq r\)
We can write \(r\div s\) as
Division Example

3.3 Generalized Projection¶
通过引入数学函数来扩展投影操作
- E是代数关系表达式
- 每一个F都是包括常数和属性的数学表达式
Example

3.4 Aggregate Functions and Operations¶
-
Aggregation function(聚合函数)takes a collection of values and returns a single value as a result.
- avg: average value
- min: minimum value
- max: maximum value
- sum: sum of values
- count: number of values
-
Aggregate operation in relational algebra \(G_1,G_2,\ldots,G_n \mathcal{G}_{F_1(A_1),\ldots F_n(A_n)}(E)\)
Aggregate Operation Example

分组结果没有名字,可以用 rename 或者 as 进行改名。
e.g. dept_name G avg(salary) as avg_sal (instructor)
3.5 Modification of the Database¶
- Deletion
- Insertion
- Updating
所有这些操作可以用assignment operator来表示
3.6 Multiset Relational Algebra¶
关系代数中,我们要求关系要是一个严格的集合。
但实际数据库中并不是,而是一个多重集,允许有重复元素存在。
因为一些操作的中间结果会带来重复元素,要保持集合特性开销很大,因此实际操作中不会去重 。
4 SQL and Relational Algebra¶
select A1, A2, ... An from r1, r2, ... rm where Pis equivalent to \(\Pi_{A_1,\ldots, A_n}(\sigma_P(r_1\times r_2\ldots r_m))\)select A1, A2, sum(A3) from r1, r2, ... rm where P group by A1, A2is equivalent to \(A_1, A_2, \mathcal{G} sum(A_3)(\sigma_P(r_1\times r_2\times\ldots r_m))\)
这里按 \(A_1,A_2\) 分组,那么结果的表中会有 \(A_1,A_2,sum(A_3)\) 三列(分组依据+分组后的聚合结果),这里我们需要的就是这三列,所以分组即可。但是假设我们只需要 \(A_1, sumA3\) 那么最后还需要投影。