Introduction¶
Operations¶
[!info] Design Principle 1.Simplicity favors regularity 2.Smaller is faster 3. make common case faster
operations of the Computer Hardware 每一条指令只能完成一个operation 每一条指令只含有三个变量 - word 32bit - doubleword 64bit 经常用的变量放到寄存器里面
1 RISC-V Registers¶
在RISC-V体系结构中,寄存器的大小为64位 ![[file-20241028125513896.png]]
1 Memory Operands¶
operands 只能是寄存器
2 Signed and Unsigned Numbers¶
对二进制补码求相反数:所有位取反加一
Operands¶
- Main memory used for composite data
- 数组,结构,动态数据
- To apply arithmetic operations
- 把数据加载到寄存器
- 把结果存储回内存
- 地址使用byte进行索引
- RISC-V 是小端的(就是低位字节排放在内存的低地址端,高位字节排放在内存的高地址端)
- RISC-V不需要数据自然对齐,但是会变慢
- 对齐:word的起始地址必须是4的倍数,doubleword的起始地址必须是8的倍数,对齐会使数据的传输更快

 RISC-V instructions
- 指令都是32位
RISC-V instructions
- 指令都是32位
Representing Instructions in the computer¶
- 计算机中的所有信息都是用二进制来表示的
- 指令也用二进制编码
- 寄存器映射到数据
- RISC-V指令
- 编码为32bit的word
- 少量格式编码操作代码
- 规整
1 Translating assembly into machine code¶
![[file-20241028160825421.png]]
2 RISC-V 指令格式¶

2.1 R 型指令¶
用于寄存器
| funct7 | rs2 | rs1 | funct3 | rd | opcode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 bits | 5 bits | 5 bits | 3 bits | 5 bits | 7 bits |
| - opcode : operation code | |||||
| - rd: destination register number | |||||
| - funct3: 3-bit function code(additional code) | |||||
| - rs1: 第一个源寄存器 | |||||
| - rs2:第二个源寄存器 | |||||
| - funct7:7-bit function code(additional code) | |||||
| ### 2.2 I-型指令 | |||||
| 用于带一个常数的指令和load指令 |
在移位指令中前六位funct6
 - rs1: source or base address register number
- immediate: constant operand, or offset added to base address
- rs1: source or base address register number
- immediate: constant operand, or offset added to base address
p 2s-complement, sign extended
2.3 S型指令¶

- rs1: 寄存器基址
- rs2: 源操作数寄存器
- immediate : offset added to base address
2.4 U-type¶
用于与高位立即数相关的操作
2.5 SB-type¶
用于条件分支指令 ![[file-20241020193641182.png]]
2.6 UJ-type¶
用于无条件分支指令(jal,jalr)
- rd用于存放链接地址(即返回地址)
- 如果跳转地址(立即数)过大,超过了 20 位,那么可以先用lui指令(后面会讲到这条指令,也会介绍类似的方法)将高 20 位数字放入临时寄存器中,然后再用jalr指令,跳转到地址 剩余的低位数字(临时寄存器) 上
2.7 Stored Program Computer¶
- Instructions represented in binary
- 指令和数据存储在内存中
- 程序在程序上操作(编译器)
3 Logical Operations¶


3.1 Shift Operations¶
 - immed 决定位置如何移动
- 左移
-
- immed 决定位置如何移动
- 左移
- slli rd, rs1, imm即rd = rs1<< imm
- 右移
- srli
3.2 And Operations¶
3.3 Or Operations¶
3.4 XOR Operations¶
4 Instructions for making decisions¶
4.1 Branch instructions¶
beq registers1, register2,L1branch if equal
bne register1,register2,L1branch if not equal
4.2 Compare Operations¶
slt x5,x19,x20 #x5=1 if x19<x20blt rs1,rs2,L1if(rs1<rs2)branch to instruction labeled L1
bge rs1,rs2,L1if (rs1>=rs2)branch to instruction labeled L1
4.3 Jump register & jump address table¶
- Jump-and-link register
jalr x1,100(x6)跳转到所给地址执行程序,exit之后执行PC+4的指令
4.4 Basic Blocks¶
A basic block is a sequence of instructions with - 没有branch跳出程序,也不会有branch突然跳到本程序的中间
所以编译器可以进行充分的优化
5 Suporting Procedures in Computer Hardware¶
进程调用的六大步骤: 1. 传入参数 2. 程序的控制权交给这个进程 3. 得到存储资源 4. 完成desired task 5. 使主程序能得到结果 6. 归还控制权
program counter(PC) :用于保存当前执行指令的地址
5.1 Procedure Call Instructions¶
- Instruction for procedures
jal x1,ProcedureAddress: 下一条指令地址在x1,跳转到目标地址 - Procedure return: jump and link register
jalr x0, 0(x1)- Like jal, but jumps to
0 + address in x1 - Use
x0as rd (x0cannot be changed) - Can also be used for computed jump
- Like jal, but jumps to
5.2 Using More Registers¶
- More Registers for prodedures calling:
- a0-a7(x10-x17):八个传参和返回值寄存器
- ra/x1:返回时的地址
- Stack
- 对于寄存器溢出,理想的数据结构是stack
- In RISC-V,the stack pointer is x2/sp
- push/pop
- Stack grow from higher address to lower address
- Push:
sp=sp-8 - pop:
sp=sp+8[!info] compiling a leaf procedure


- Push:
5.3 Nested Procedures¶
同样是压栈\(\rightarrow\)出栈
[!note] procedure ![[file-20241020193257872.png]]
![[file-20241020194218195.png]] todo 父函数保证:子函数能随便使用temporary registers,返回给父函数的时候,值可以被改变 子函数保证:返回给父函数的时候,saved registers 保持父函数调用子函数前的值
6 Local Data on the Stack¶
在栈上给新数据分配内存
- 过程帧(procedure frame)/活动记录(activation record):栈内的一段空间,里面存储了过程所需的寄存器和变量 。
- 寄存器x8(或者称为fp)是一个帧指针(frame pointer),它指向过程帧内第一个double word。
- 栈指针会随着过程的进行而不断变化,因此在过程的不同阶段访问同一个变量或寄存器时,用到的偏移量会不断变化,从而带来理解上的不便
- 而帧指针在过程中为局部变量提供一个稳定的基址寄存器
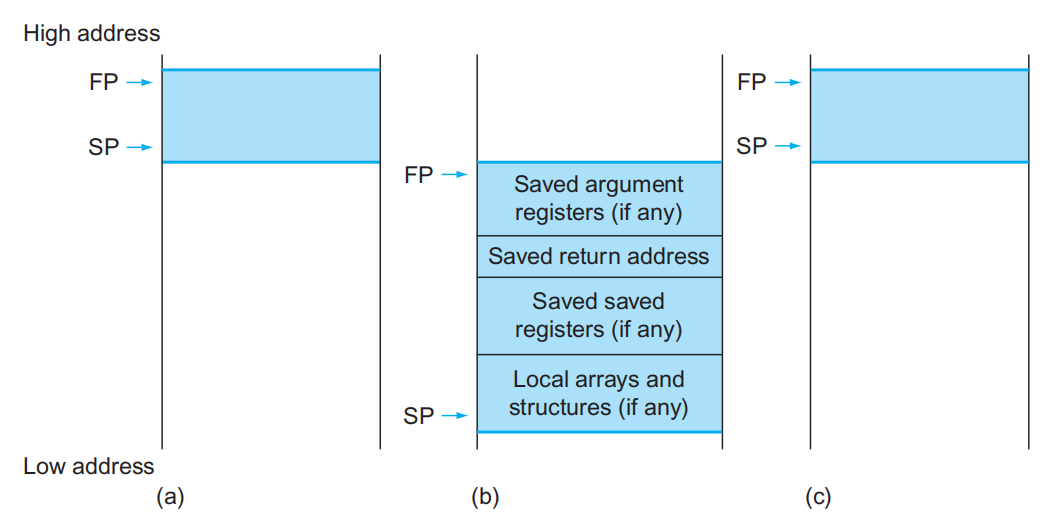
-
寄存器
x3(或者称为gp)是一个全局指针(global pointer),它指向的是静态 (static) 数据。 -
Linux 系统上 RISC-V 的内存分配示意图:
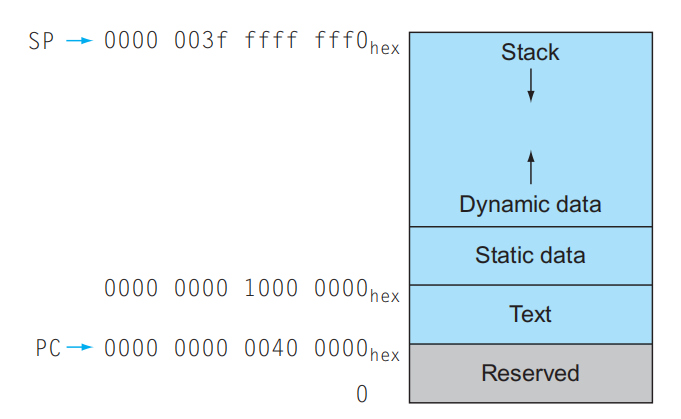
- 最底下的内存是保留的空间(不可访问)
- 第二层的内存用于存放 RISC-V 的机器码,称为文本段(text segment)
- 第三层的内存称为静态数据段(static data segment),用于放置立即数和其他静态变量
- 最上层同时存放栈和动态数据(比如链表等),其中存放动态数据的数据结构称为堆(heap)。注意到栈和堆位于这块内存的两端,分别自顶向下和自底向上增长
- C 语言中使用
malloc()在堆中分配空间,使用free()释放堆内的空间。如果过晚释放空间,就会造成内存泄露问题;如果过早释放空间,就会造成悬空指针 (dangling pointers)(类似野指针)问题。 ![[file-20241028190531928.png]]
- C 语言中使用
Communicating with people character data¶
-
Byte-encoded character sets
- ASCII
- Latin-1
- Unicode: 32-bit character set
1 Byte/halfword/word Operations¶
- RISC-V byte/halfword/word load/store
lb rd, offset(rs1)- `lh rd, offset(rs1)
lw rd, offser(rs1)![[file-20241021131319049.png]][!note] Strcpy Example ![[file-20241021131810673.png]] ![[file-20241021131827015.png]]
Addressing¶
1 RISC-V Addressing for 32-bit Immediate and Addresses 超大立即数加载¶
虽然在大多数情况下,立即数不会很大(≤\(2^12\)),能够直接存在指令中;但如果超过 12 位,RISC-V 会用lui (load upper immediate) 指令来处理这类较大的立即数。
lui的指令格式为 U-type- 它可以加载立即数的高 20 位,将其放入寄存器中间的第 12 位到第 31 位,寄存器的低 12 位用 0 填充,高 32 位用第 31 位上的数字填充
- 举个例子:要将 32 位立即数赋给寄存器,可以先用
lui指令将高 20 位赋给寄存器,之后用addi指令将剩余的 12 位加到寄存器中(具体见下面的“例题”)
2 Addressing Mode¶
![[file-20241021134200405.png]]
2.1 Branch Addressing¶
默认立即数末尾补0,分支指令是PC相对寻址
![[file-20241021133413404.png]]2.2 Jump Addressing¶
![[file-20241021133439755.png]] ![[file-20241021133517443.png]] branch指令的offset最后一位是符号位 - 虽然大部分的跳转地址离分支指令都比较近(根据 SPEC 测试,一半左右的分支指令跳转距离不超过 16 条指令),但是仍会存在一些跳转距离很远,超过 12 位地址的指令。这时汇编器会采取以下挽救措施: - 插入一条无条件分支指令,它的跳转地址即为目标跳转地址 - 将原来条件分支指令的条件取反,让条件分支语句自行决定是否跳过无条件分支
[!note] example
beq x10,x0,L1如果L1地址过远,这条指令将被替换成以下指令:
2.3 Summary¶
寻址模式(addressing mode):决定此架构下机器语言指令对于的运算数 ![[file-20241021132629772.png]] - 立即寻址(immediate addressing):操作数为指令内的立即数 - 寄存器寻址(register addressing):操作数为寄存器 - 基址或偏移寻址(base or displacement addressing):操作数位于指定的内存位置上,该位置是寄存器和立即数之和 - PC 相对寻址(PC-relative addressing):分支地址为 PC 和分支偏移量(立即数的 2 倍)之和 \(\(\begin{align}Target~address=&PC+Branch~offset\\=&PC+immediate\times 2\end{align}\)\)
3 Decoding assembly code¶
- 确定opcode
- 确定其他的区域
- 翻译为汇编语言
[!info] example ![[file-20241021134456795.png]]
3.1 Summary¶
![[file-20241021134532644.png]] ![[file-20241021134543756.png]] ![[file-20241021134554625.png]]
4 RISC-V中的同步¶
- 两个进程使用一片内存
- P1 writes, then P2 reads
- Data race 如果P1 P2 没有同步
- 硬件支持
- 原子读写操作
- 读写之间不允许访问这块地址
有些处理器有专门实现原子操作的指令,比如原子交换 (atomic swap/exchange)(实现寄存器和内存数据的交换)等。而 RISC-V 提供了一个指令对 (instruction pair) lr.d和sc.d:
-
lr.d(load-reserved doubleword):-
格式:
lr.d rd, (rs1) -
功能:将存储在寄存器
rs1的内存地址上的数据加载到寄存器rd上,同时保留这块内存地址,除sc.d的其他指令不应该访问这块地址
-
-
sc.d(store-conditional doubleword):- 格式:
sc.d rd, rs1, (rs2) - 功能:
- 将寄存器
rs1上的数据放入存储在寄存器rs2的内存地址上 - 并且由寄存器
rd指示该指令是否成功:若成功,则rd = 0,否则rd为一个非零值(表示有其他指令访问过这块内存空间)[!note] Example1:原子交换
[!note] Example2:加锁&解锁 ``` addi x12, x0, 1 again: lr.d x10, (x20) bne x10, x0, again sc.d x11, x12, (x20) bne x11,x0,again sd x0, 0(x20)
- 将寄存器
- 格式:
5 Translating and starting a program¶
==to do ==
6 Arrays versus Pointers¶
7 MIPS Instructions¶
8 x86 Instructions¶
9 其他RISC-V指令¶
![[file-20241021144153007.png]] - M: integer multiply, divide , remainder - A: atomic memory operations - F:single-precision floating point - D: double-precision floating point - C: compressed instructions - 16-bit encoding for frequently used instructions