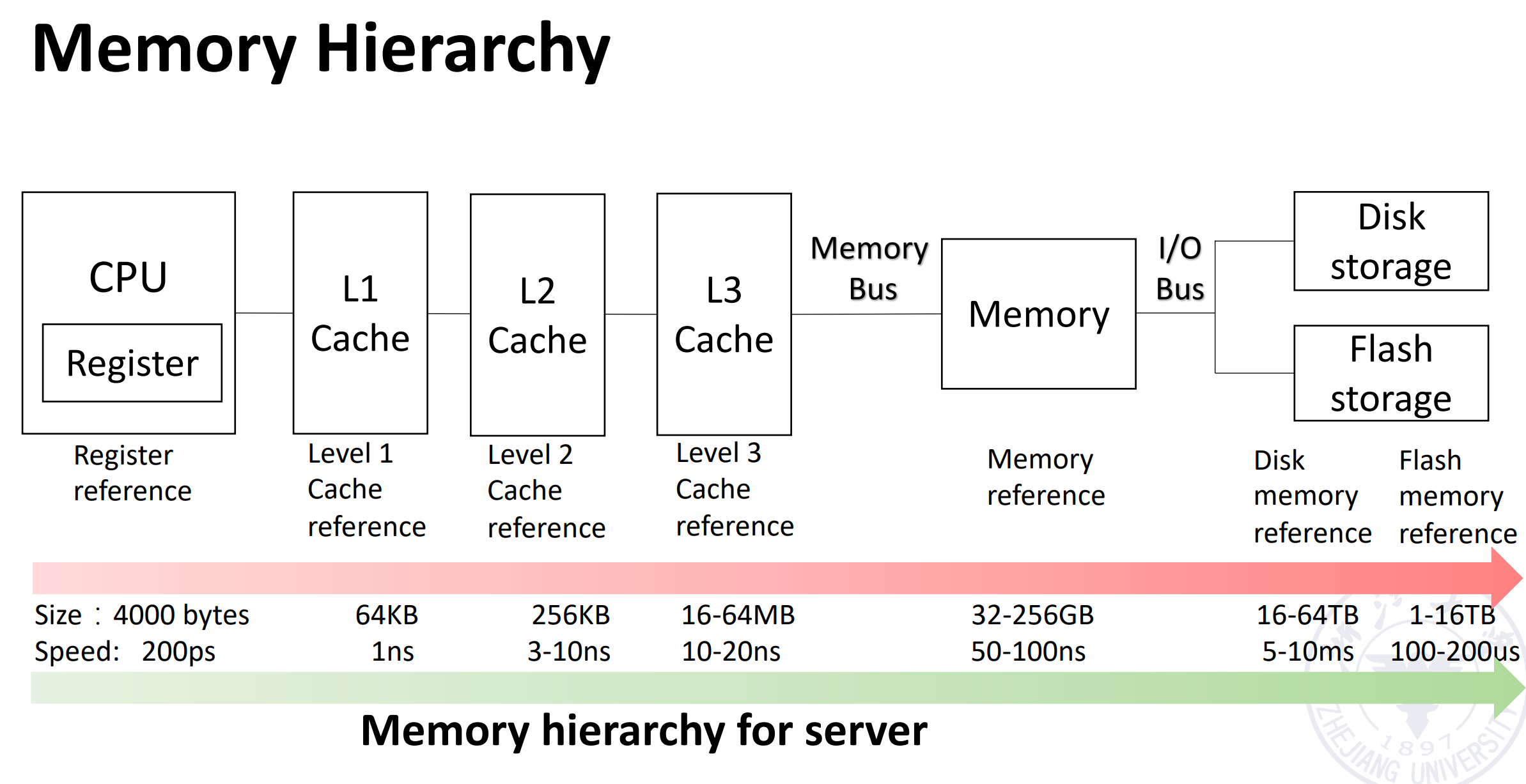
Memory Hierachy¶
1 Introduction¶
1.1 Memory¶
内存层次:
- Register
- Cache
- Memory
- Storage
存储技术:
- Mechanical Memory
- Electronic Memory
- SRAM
- DRAM
- SDRAM
- DDR
- GDRAM
- GDDR
- HBM
- EPPROM
- NAND
- NOR
- Optical Memory
1.2 Cache Concept¶
Cache: a safe place for hiding or storing things.
采用缓冲技术来重复使用频繁出现的项目。
-
Cache Hit/Miss: When the processor can/cannot find a requested data item in the cache一个包含被请求字的固定大小的数据集合,它从主内存中取出并放入缓存中。
Cache Miss 会带来额外的开销:由 Latency, Bandwith 决定。
-
Cache Block/Line: A fixed-size collection of data containing the requested word, retrieved from the main memory and placed into the cache.
-
Cache Locality:
-
Temporal locality: need the requested word again soon
访问过这个数据,之后很可能再次访问这个数据。
-
Spatial locality: likely need other data in the block soon
访问了这个位置,之后很可能访问下一个位置。
-
36 terms of Cache
1.3 Three classes of computers with different concerns in memory hierarchy¶
- Desktop Computers 更关心内存层次结构的平均延迟
- Server Computers 关心内存带宽
- Embedded Computers: 更关心功率和电池寿命
1.4 Enhance speed of memory¶
Component character of hardware: - 硬件越小,成本越高,速度越快 - 更大的内存更便宜
1.5 The method enhance speed of memory¶
利用局部性原则: - Temporary locality: 使最近访问的数据更靠近处理器 - Spatial locality: 将最近访问的连续数据块移近处理器
The method
- Hierarchies bases on memories of different speeds and size
- The more closely CPU the level is, the faster the one is.
- The more closely CPU the level is, the smaller the one is.
- The more closely CPU the level is, the more expensive one is.
2 Four Questions for Cache Designers¶
这部分内容可见计组笔记
Caching is a general concept used in processors, operating systems, file systems, and applications.
- Q1: Where can a block be placed in the upper level/main memory? (Block placement)
- Fully Associative, Set Associative, Direct Mapped
- Q2: How is a block found if it is in the upper level/main memory? (Block identification)
- Tag/Block
- Q3: Which block should be replaced on a Cache/main memory miss? (Block replacement)
- Random, LRU,FIFO
- Q4: What happens on a write? (Write strategy)
- Write Back or Write Through (with Write Buffer)
2.1 Q1: Block Placement¶
-
Direct mapped
一个块在 cache 中有一个固定的位置(通常通过取模得到)。
-
Fully associative
块可以放在 cache 里的任意位置。(不好找)
-
Set associative
- 块可以在一个组里的任何位置,组里可以放若干个块。
- 直接映射相当于一路组相联,全相联相当于 n 路组相联(n 是 cache 的块数)
一般情况,\(n\leq 4\)
The higher the degree of association, the higher the utilization of cache
space, the lower the probability of block collision and the lower the
failure rate.
关联度越高,缓存空间的利用率就越高,块冲突的概率就越低,失败率也就越低。
2.2 Q2: Block Identification¶

2.3 Q3: Block Replacement¶
- Random replacement - randomly pick any block
-
Least-Recently Used (LRU) - pick the block in the set which was least recently accessed
需要额外的位数来记录访问的时间。一般我们用的是近似的 LRU。
-
First In, First Out (FIFO) - Choose a block from the set which was first came into the cache
Strategy of Block Replacement
Suppose:
-
Cache block size is 3, and access sequence is shown as follows.
2, 3, 2, 1, 5, 2, 4, 5, 3, 4
-
FIFO, LRU and OPT are used to simulate the use and replacement of cache block. (OPT 是一种理想情况,用来衡量算法性能)
-
FIFO
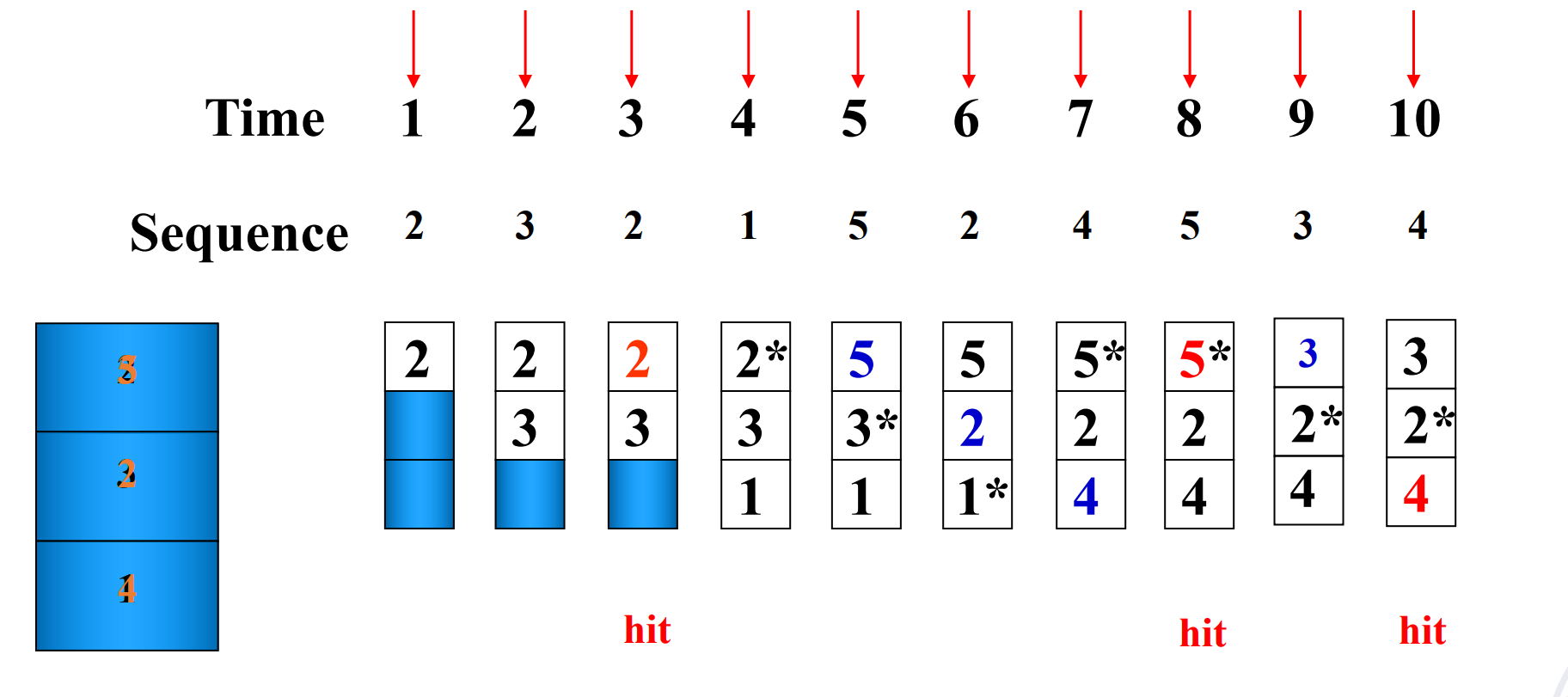
-
LRU
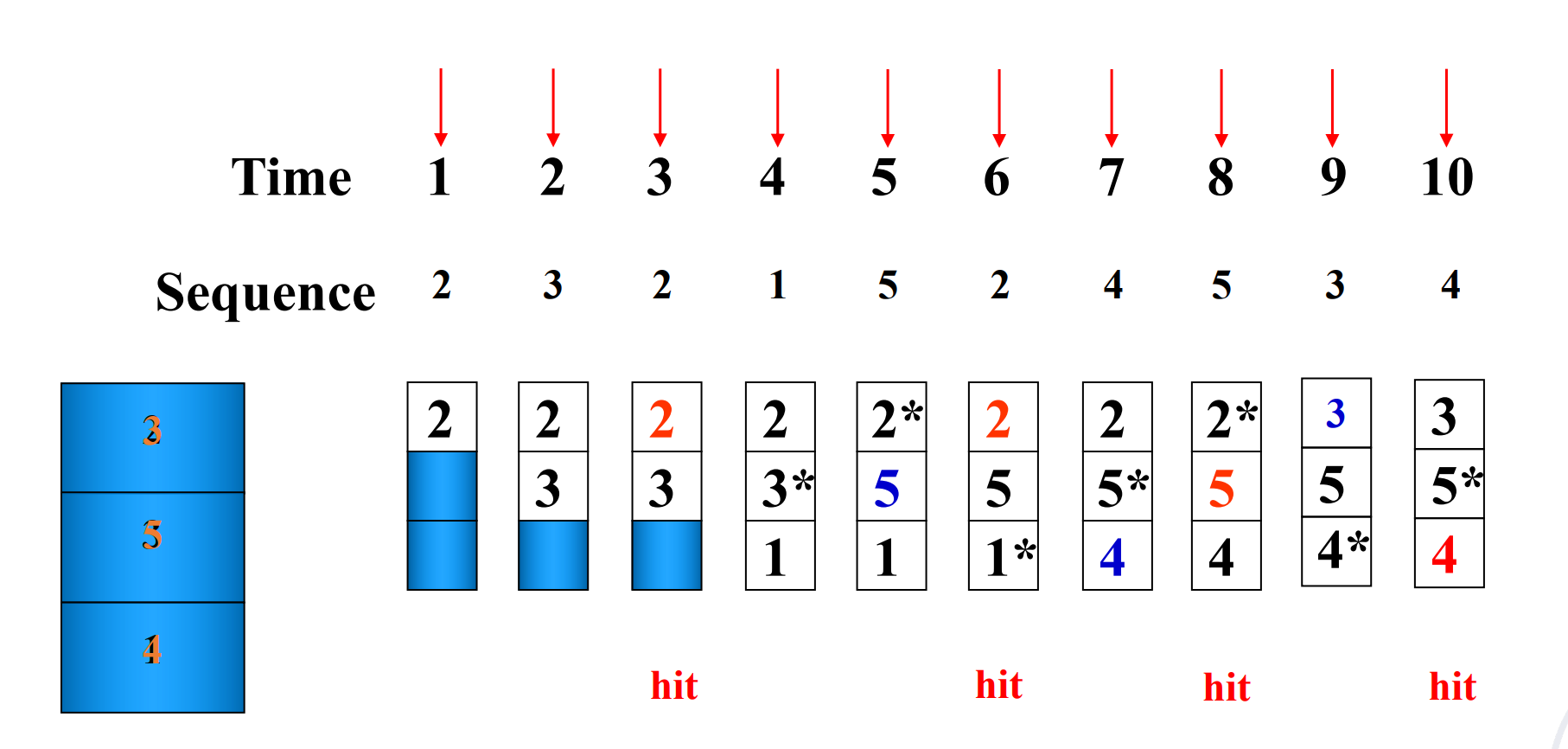
-
OPT
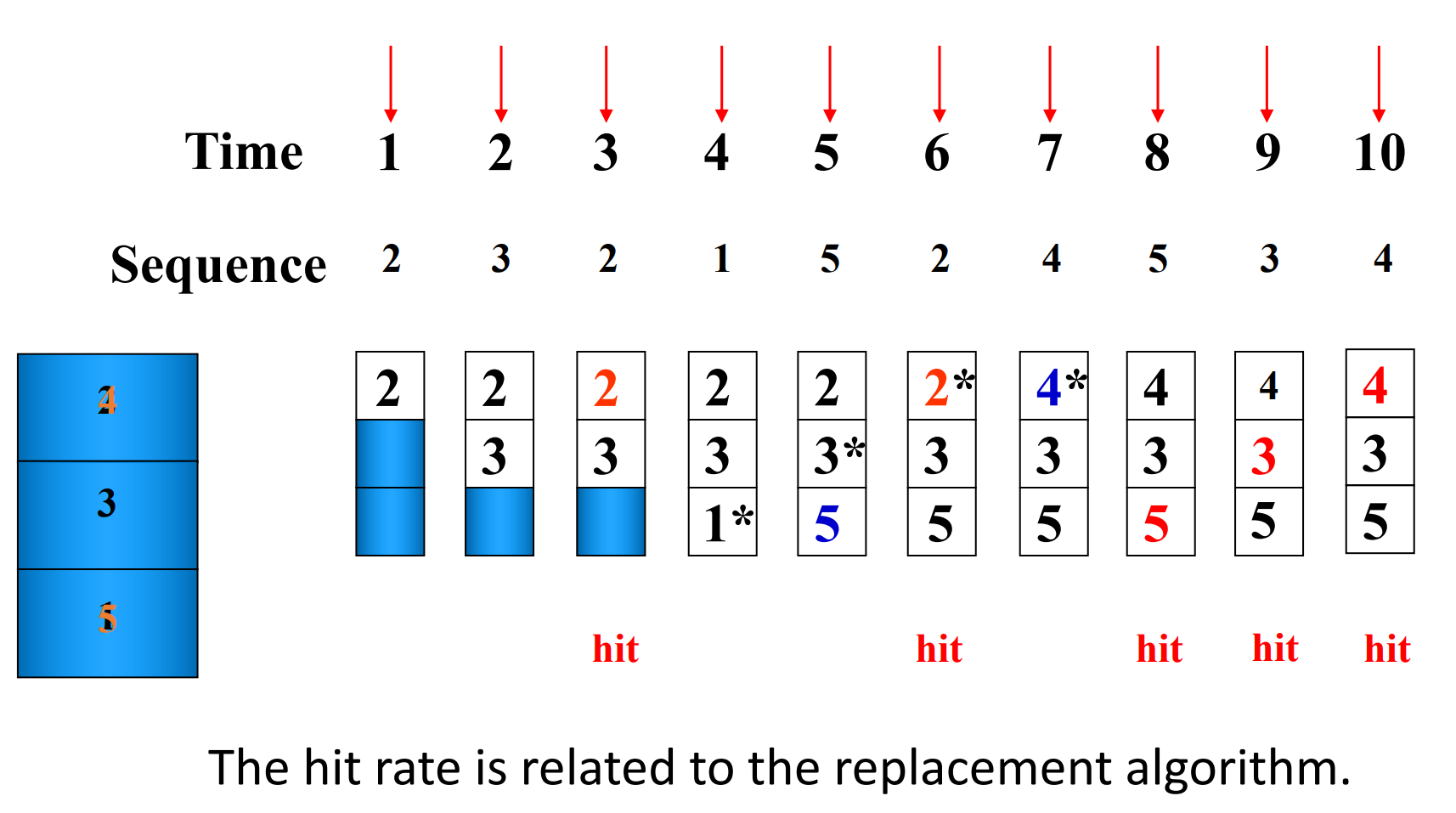
-
Hit rate is related to the replacement algorithm, the access sequence, the cache block size.
2.3.1 Stack replacement algorithm¶
有些算法随着 N 增大命中率非下降,有些算法随着 N 增大命中率反而会下降。
我们把随着N 增大命中率非下降的算法称为 stack replacement algorithm。
\(B_t(n)\) represents the set of access sequences contained in a cache block of size \(n\) at time \(t\).
- \(B_t(n)\) is the subset of \(B_t(n+1)\).
LRU replacement algorithm is a stack replacement algorithm, while FIFO is not.
For LRU algorithm, the hit ratio always increases with the increase of cache block.
Using LRU
用栈来模拟 LRU,栈顶是最近访问的,栈底是最久未访问的,每次要替换的时候,替换栈底的元素。通过下面的图可以快速看到栈大小为 n 时的命中率。

2.3.2 LRU Implementation - Comparison Pair Method¶
如何只通过门和触发器来实现 LRU 算法?—— Comparison Pair Method
-
Basic idea
Let each cache block be combined in pairs, use a comparison pair flip-flop to record the order in which the two cache blocks have been accessed in the comparison pair, and then use a gate circuit to combine the state of each comparison pair flip-flop, you can find the block to be replaced according to the LRU algorithm.
让任何两个 cache 块之间两两结对,用一个触发器的状态来代表这两个块的先后访问顺序(比如 1 表示 A 刚被访问,0 表示 B 刚被访问)。通过门电路对触发器的状态进行逻辑组合,找到最久未被访问的块。
Comparison Pair Method
这里有 3 个 cache blocks A, B, C。那么我们需要 3 个触发器来记录之间的状态。假设 \(T_{AB}=1\) 表示 A 被更近访问,\(T_{AC}, T_{BC}\) 同理。

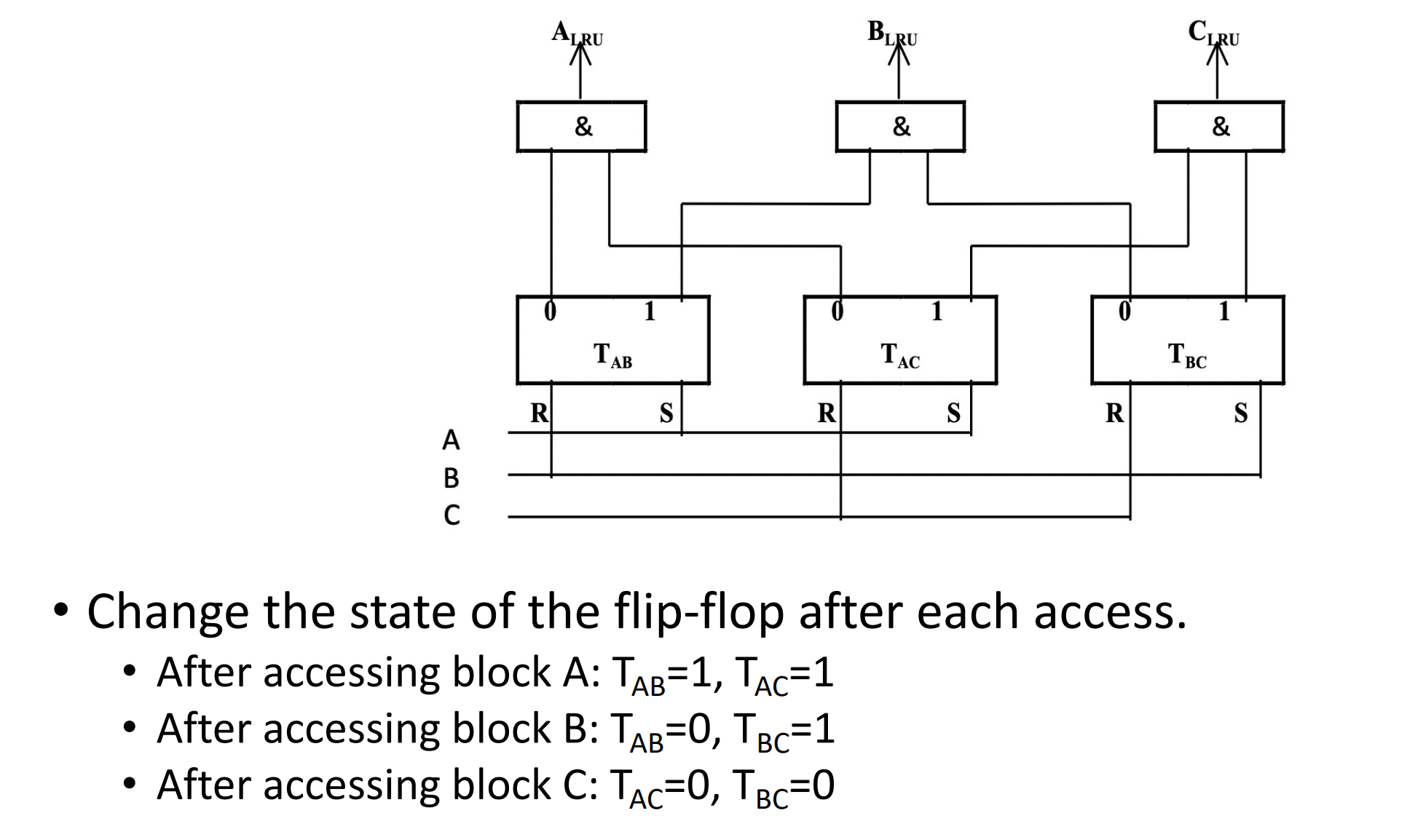
-
Hardware usage analysis
假设有 p 个 cache blocks, 我们需要 \(C_p^2=p\cdot (p-1)/2\) 个触发器。
当 \(p\) 超过 8 时,需要的触发器过多,这个算法就不适用了。
2.4 Q4: Write Strategy¶
-
Write Hit
-
Write Through:直接写回到内存。
写到内存的时间较长,这个过程需要 Write Stall,或者使用 Write Buffer。

-
Write Back:在 Cache 中写,同时通过一个额外的 dirty bit 表示这个块已经被修改但并未写回下一级内存中。
-
-
Write Miss
- Write Allocate:将要写的块先读到 Cache 中,再写。
- Write Around:直接写到内存。
- In general, write-back caches use write-allocate , and write-through caches use write-around.
Example

Read Strategy:
- Read through: 可以直接读cache内存中的
- Read allocate: 先从memory中读到cache中

3 Memory System Performance¶
这部分也可见计组笔记
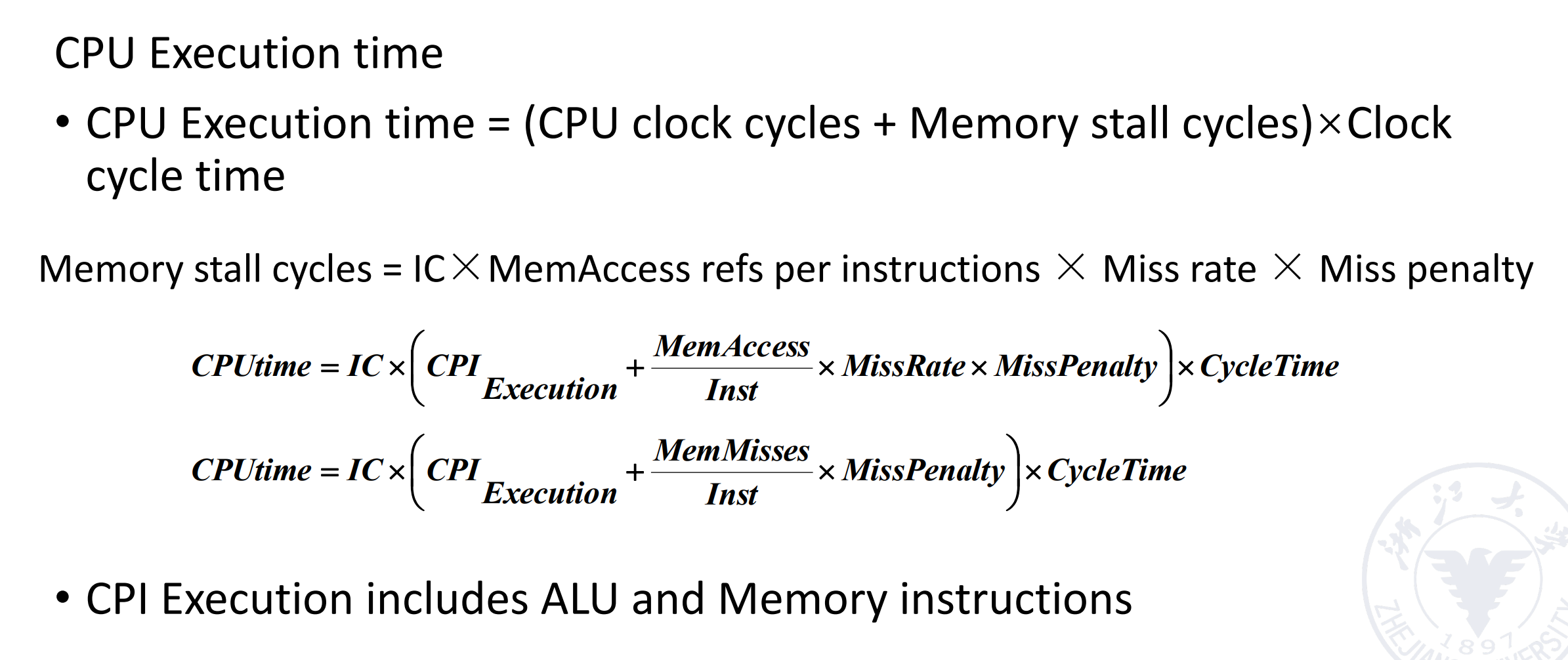
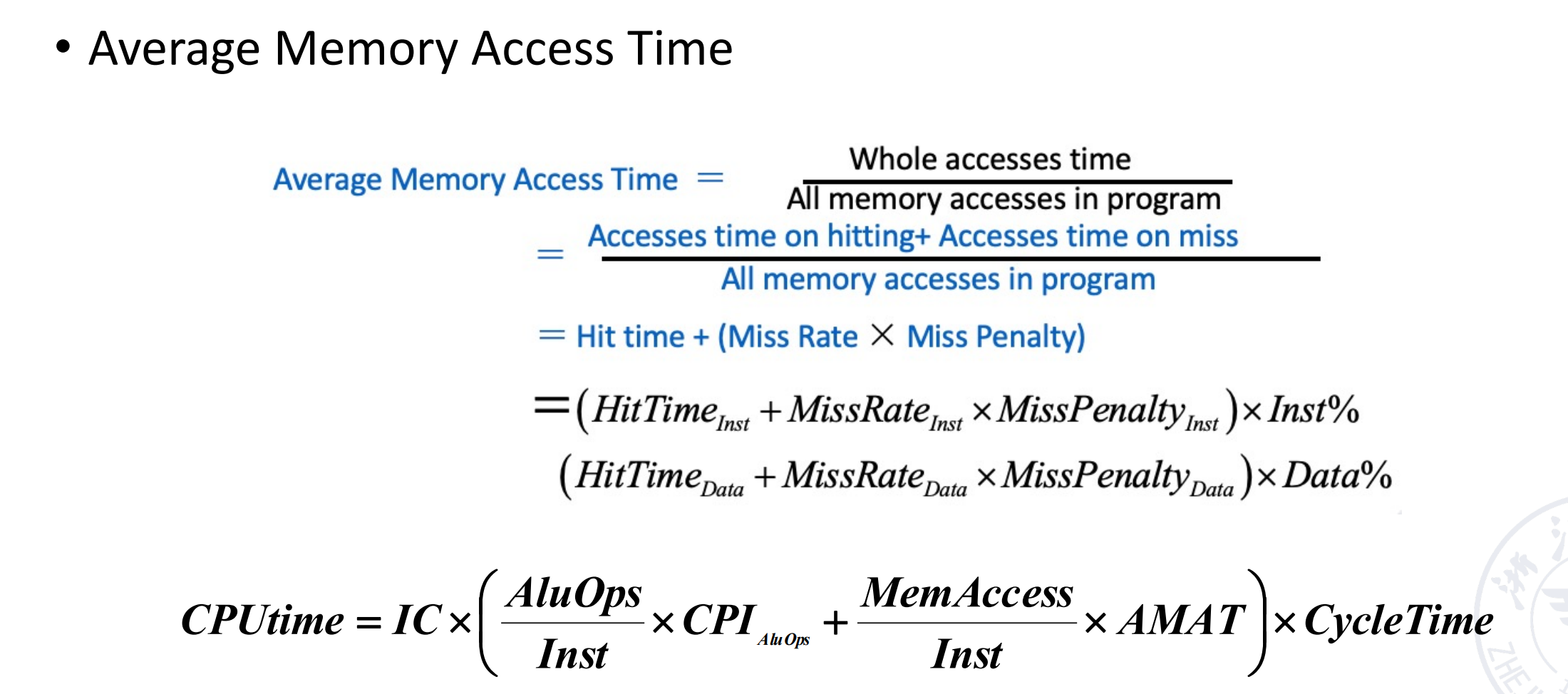
How to improve
- Reduce the miss penalty
- Reduce the miss rate
- Reduce the time to hit in the cache
- Reduce the miss penalty and miss rate via parallelism
4 Virtual Memory¶
物理内存有限,虚拟内存让用户体验到一个抽象的更大的内存。
-
Why virtual memory?
可以让进程使用不连续的物理内存空间(虚拟地址上是连续的);更好地隔离不同进程。
-
virtual-physical address translation
- memory protection/sharing among multi-program
Virtual Memory = Main Memory + Secondary Storage
-
Virtual Memory Allocation
-
Paged virtual memory
page: fixed-size block
-
Segmented virtual memory
segment: variable-size block
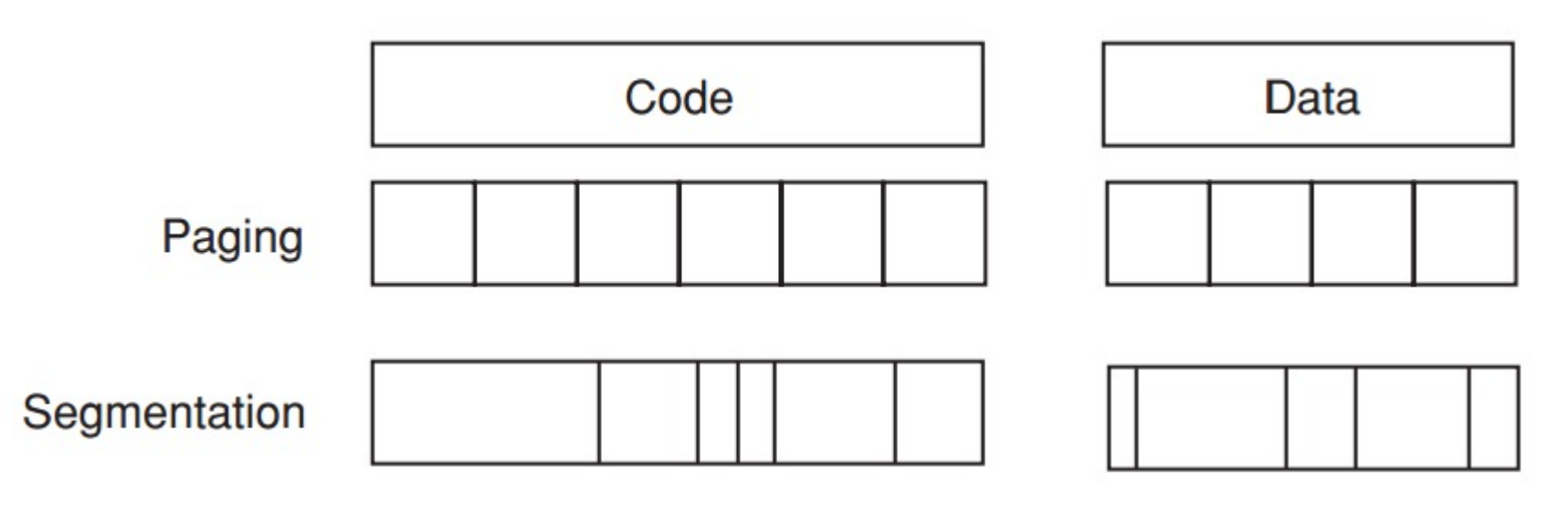
-
Paging vs Segmentation
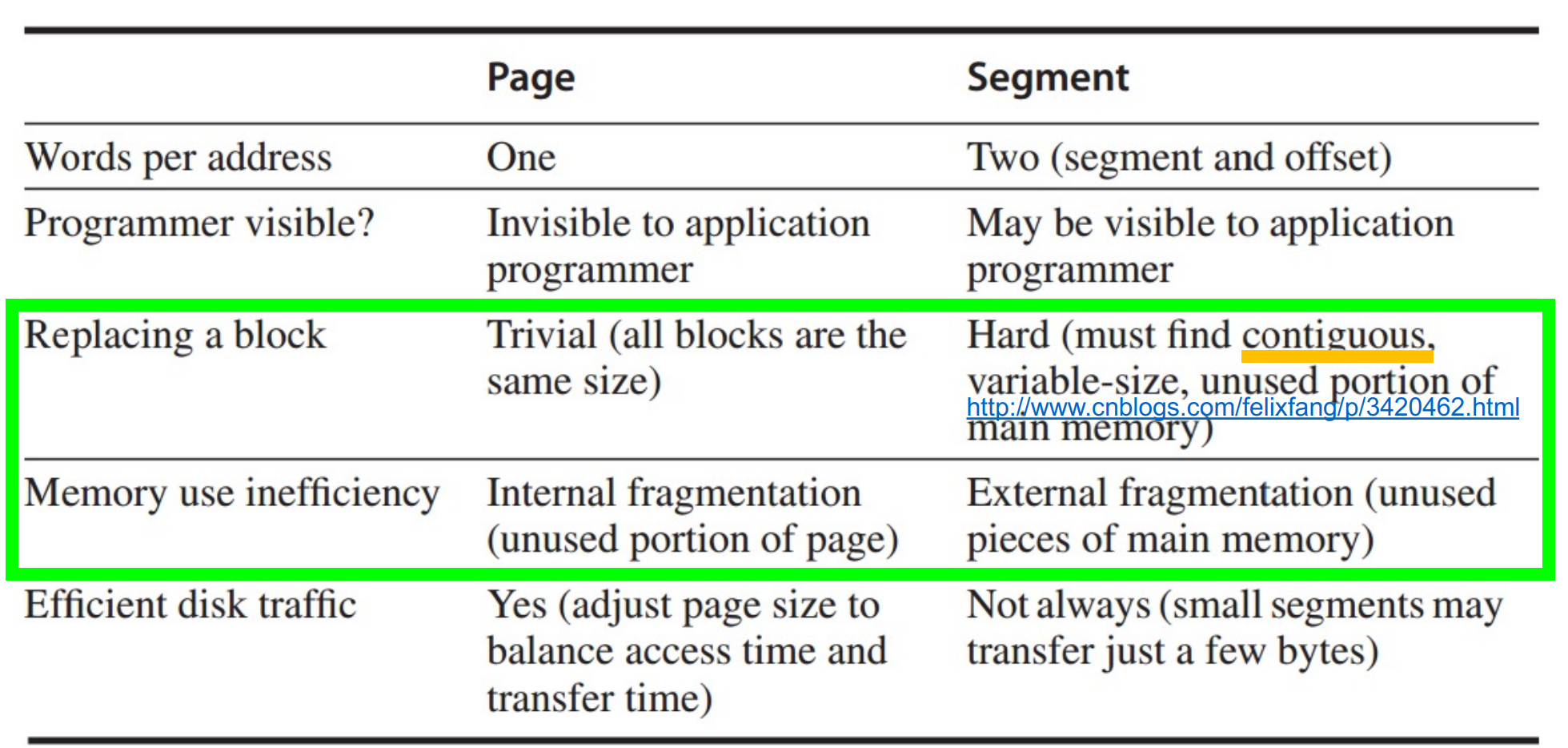
分页式的易于实现,方便替换。现在常用段页式结合,或者纯页式。
4.1 How virtual memory works?¶
Cache 的四个问题在虚拟内存中都有对应。
-
Q1. Where can a block be placed in main memory?
缺失代价很高,因此我们采用全相联的方式,以降低 miss rate。
-
Q2. How is a block found if it is in main memory?
虚拟地址分两部分,偏移量和页号。页号是页表的索引。
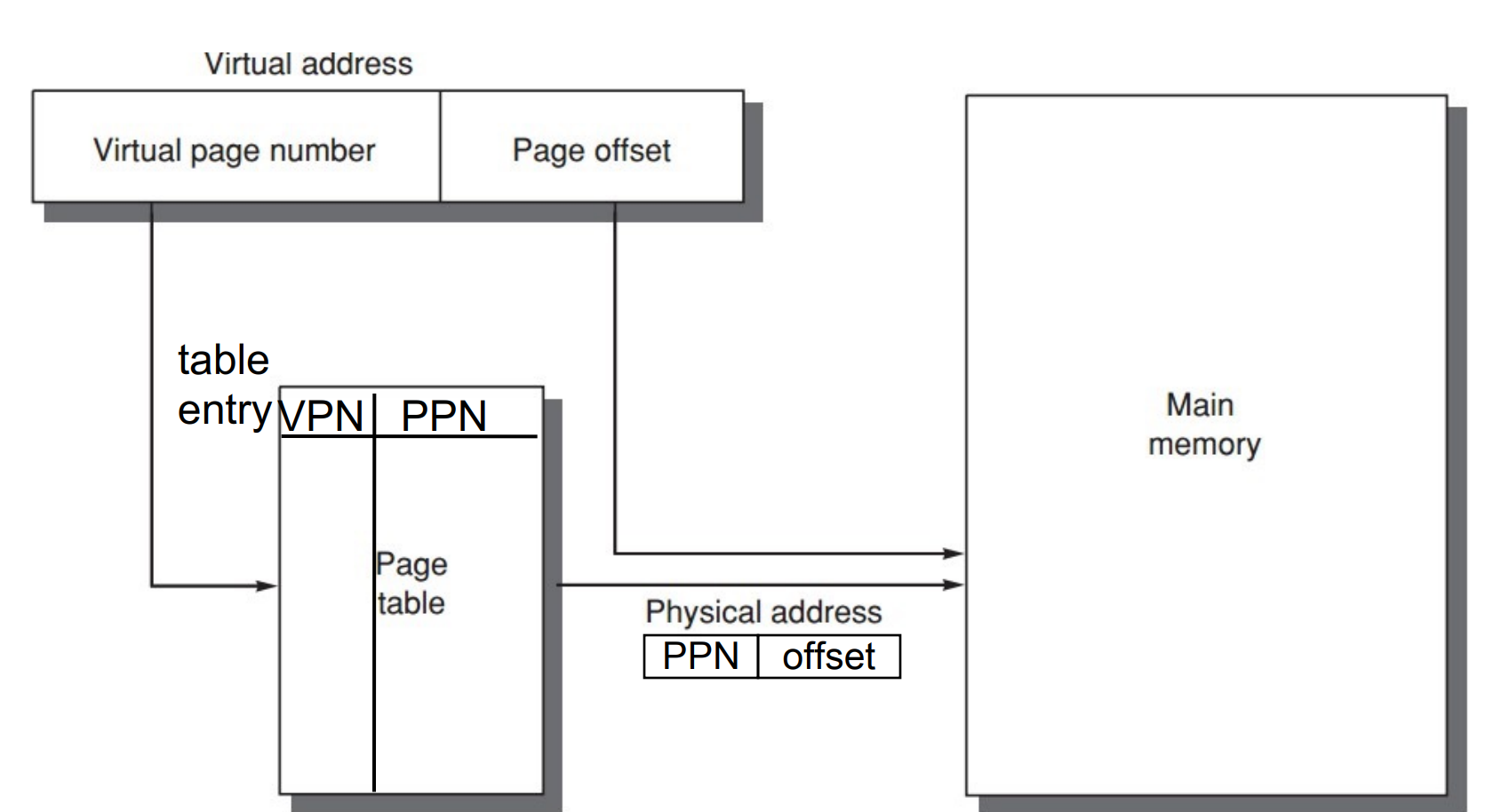
-
Q3. Which block should be replaced on a virtual memory miss?
Least Recently Used (LRU) block, with use/reference bit.
-
Q4. What happens on a write?
Write-back strategy, with diry bit. 往disk上写的代价太大
4.2 Page Table¶
-
Page tables are often large
e.g. 32-bit virtual address, 4KB pages, 4 bytes per page table entry.
page table size: \((2^{32}/2^{12}) \times 2^2 = 2^{22}\) bytes = \(4\) MB -
page table存储在main memory中
-
Logically two memory accesses for data access 两次访存:
- one to obtain the physical address from page table;
- one to get the data from the physical address;
正常来说页表需要两次内存访问,访问效率低下,因此我们需要 cache page table,即 TLB(块表)。
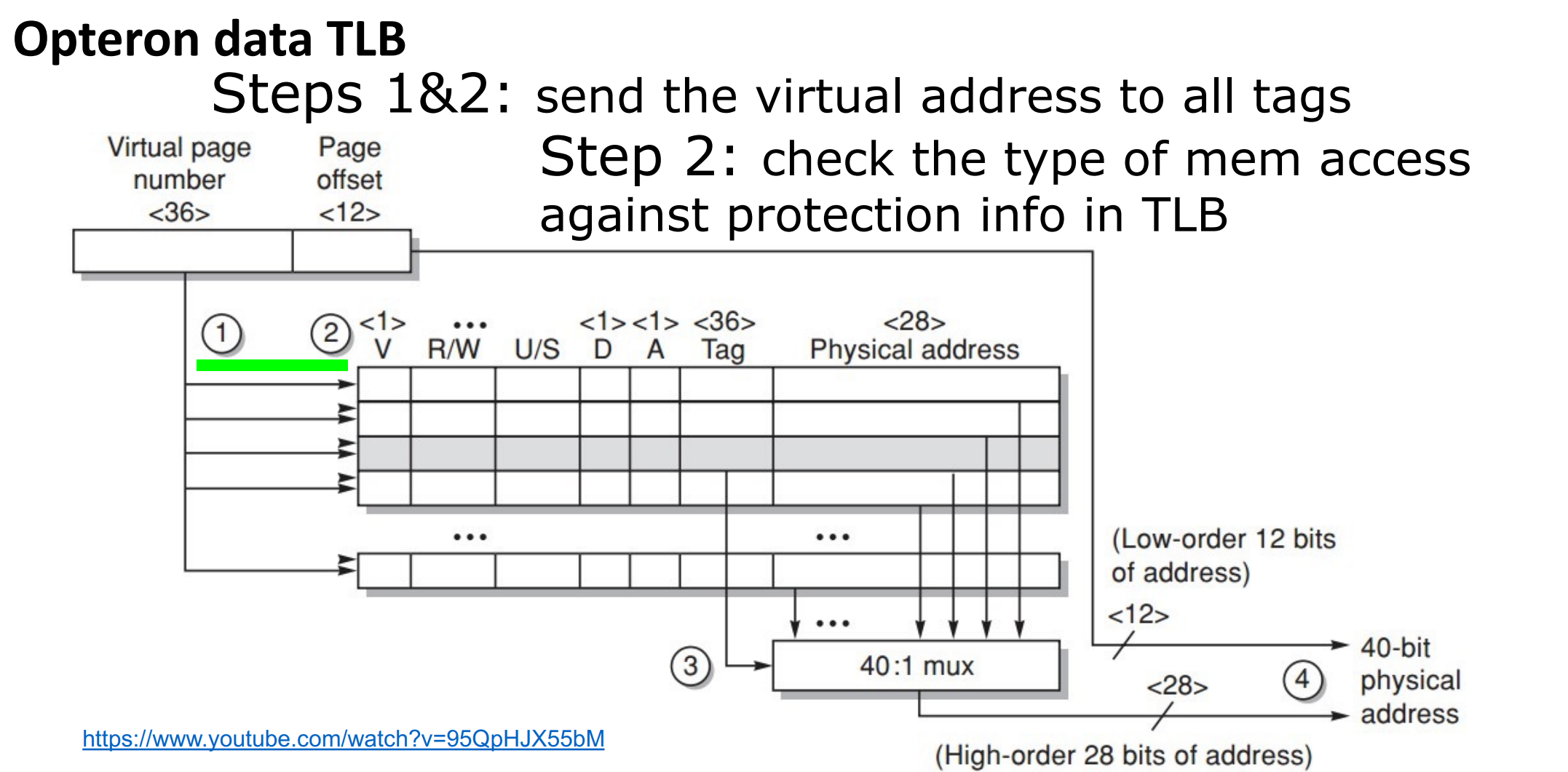
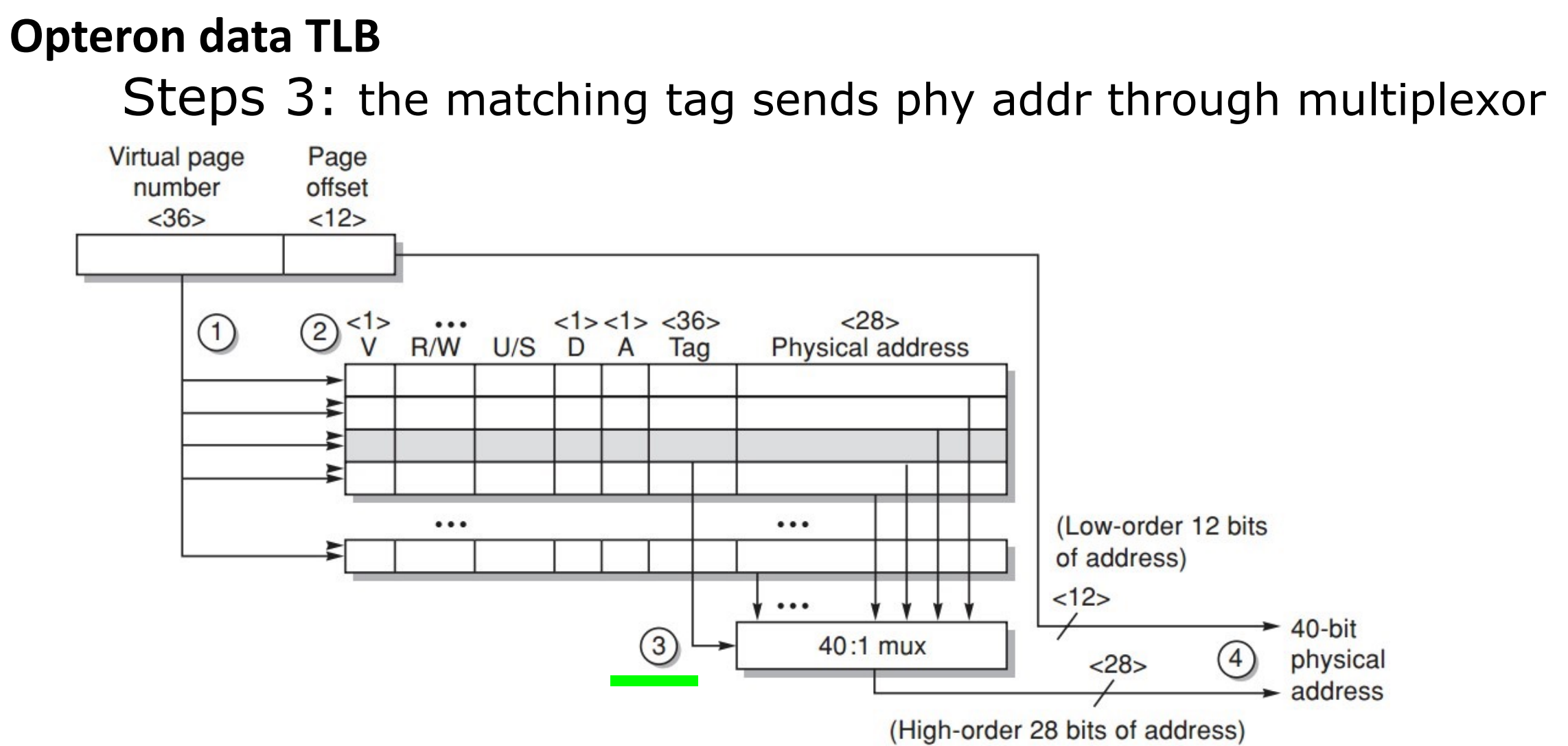
Translation lookaside buffer (TLB)
- tag: portions of the virtual address (VPN);
- data: a physical page frame number (PPN), protection field, valid bit, use bit, dirty bit;
Example
发送 tag (VPN) 尝试匹配,并看访问类型是否违规。如果匹配成功,就把对应的 PPN 送到 Mux,将偏移量加上 PPN 得到物理地址。

4.3 Page Size Selection¶
-
Pros of larger page size
-
Smaller page table, less memory (or other resources used for the memory map);
页更少,所以页表更小。
-
Larger cache with fast cache hit;
页更大,所以 cache 命中的时间更短(因为我们需要遍历的页更少)。
-
Transferring larger pages to or from secondary storage is more efficient than transferring smaller pages;
一次搬运更多的数据,所以更高效,小页可能需要搬运多次。
-
Map more memory, reduce the number of TLB misses;
TLB miss 次数更少。
-
-
Pros of smaller page size
-
Conserve storage
When a contiguous region of virtual memory is not equal in size to a multiple of the page size, a small page size results in less wasted storage.
减少对内存的使用,内部碎片更少。
-
Use both: multiple page sizes
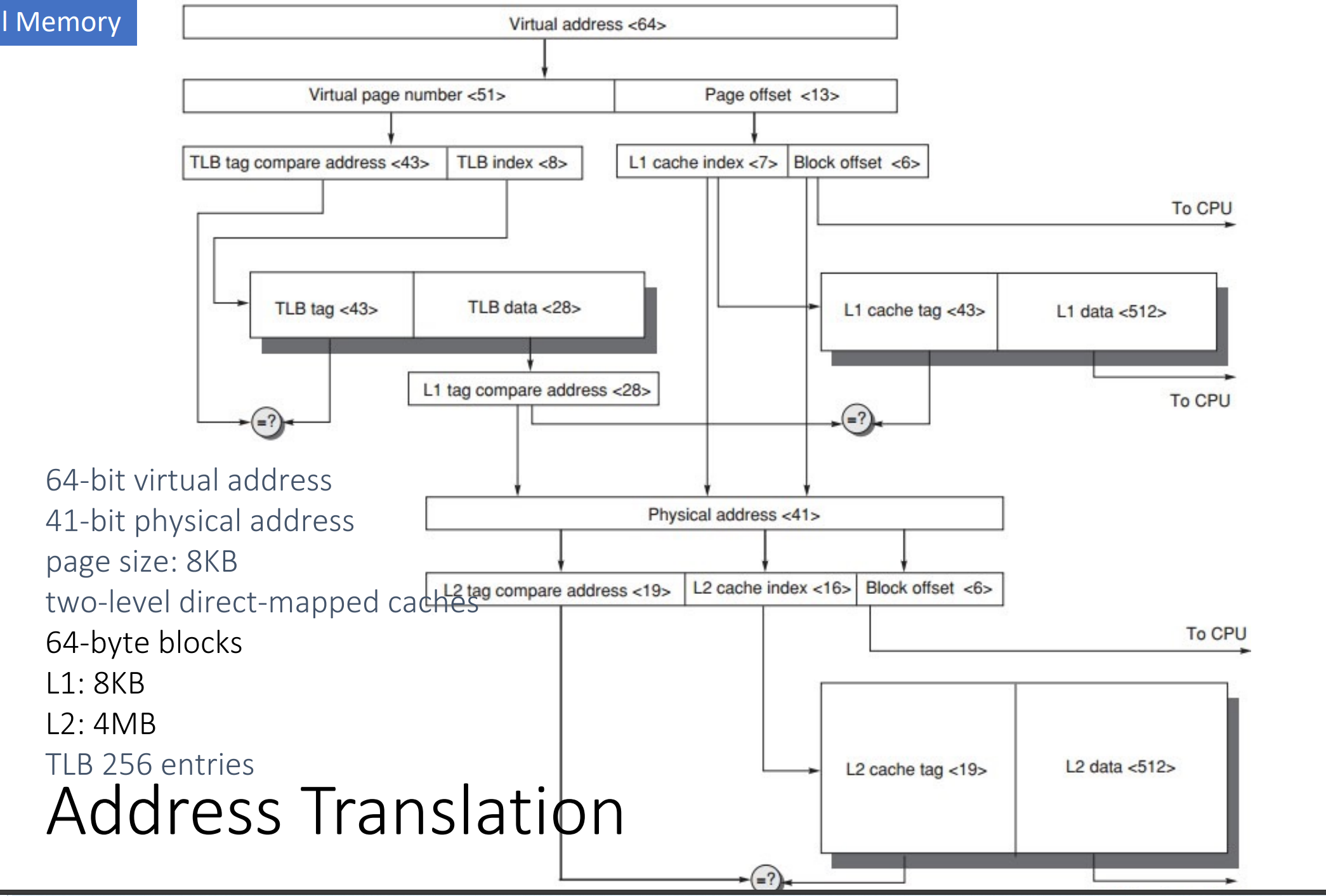
Address Translation
4.4 Multiprogramming¶
使计算机能够同时被多个程序同时运行,需要多个程序之间的保护和共享
process:
A running program plus any state needed to continue running it
一个运行中的程序加上使他运行需要的任何状态
- Time-Sharing: shares processor and memory with interactive users simultaneously; gives the illusion that all users have their own computers
- Process/Context Switch: 从一个进程到另外一个
- Maintain correct process behavior
- computer designer must ensure that the processor portion of the process state can be saved and restored;计算机设计者必须确保进程的处理器部分可以被保存
5 Summary¶
Summary
-
Memory hierarchy
- From single level to multi level
- Evaluate the performance parameters of the storage system (average price per bit C; hit rate H; average memory access time T)
-
Cache basic knowledge
- Mapping rules
- Access method
- Replacement algorithm
- Write strategy
- Cache performance analysis
-
Virtual Memory (the influence of memory organization structure on Cache failure rate)